FIGURE 4.
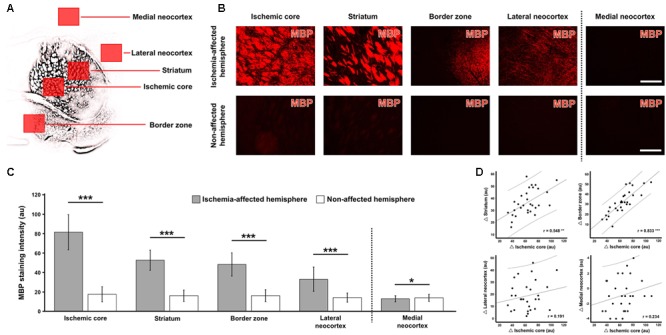
Quantification of myelin basic protein (MBP)-immunoreactivity in different brain areas 1 day after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Using a shell-like pattern, five regions of interest were arranged on the ischemia-affected hemisphere, as exemplarily shown in panel (A) based on a schematic depiction of the respective MBP-immunosignal, while mirrored regions to the contralateral, non-affected hemisphere served as controls. The direct inter-hemispheric comparison revealed a remarkable increase of the MBP-immunoreactivity due to ischemia in all four regions reached by ischemia (B, exemplarily captured in a 3-month-old mouse), which was confirmed by quantitative analyses (C). Subsequent correlative analyses of inter-hemispheric differences (Δ values, D) indicated simultaneous alterations of the MBP-immunosignal in the ischemic core and in the striatum as well as in the border zone. Scale bars (also valid for all other micrographs) = 200 μm: significance levels: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001; sample sizes: n = 29 – 30 for inter-hemispheric comparison (C), and n = 29 – 30 for correlation analyses (D). au, arbitrary units.
