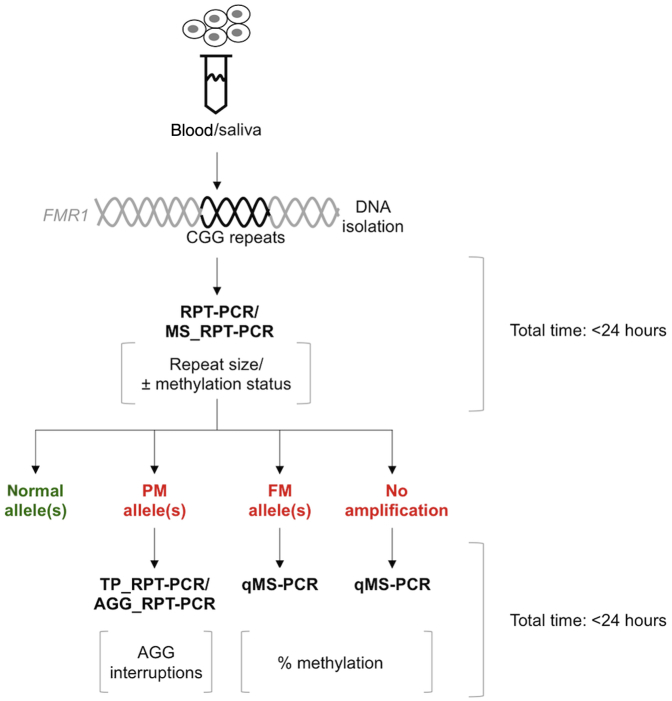
Figure 6.
Diagram illustrating the work-flow for the analysis of FMR1 alleles. RPT-PCR/MS_RPT-PCR enables the determination of repeat size and gives an indication of the methylation status for full mutation (FM) carriers. It can also reveal skewed X-inactivation in female premutation (PM) and FM carriers. Agarose gel electrophoresis can be used for rapid evaluation of alleles followed by capillary electrophoresis for samples for which an accurate repeat number is necessary. PM alleles can be further processed by either TP_RPT-PCR or AGG_RPT-PCR to determine AGG interruption status or number of uninterrupted CGG repeats at 3′ end of the repeat tract. The remaining RPT-PCR product can be used without further purification for the AGG_RPT-PCR assay if necessary, thus saving time and sample. FM alleles or alleles that were not amplified in the RPT-PCR (with or without a heat pulse) should then be processed by qMS-PCR to quantitate the amount of methylation.