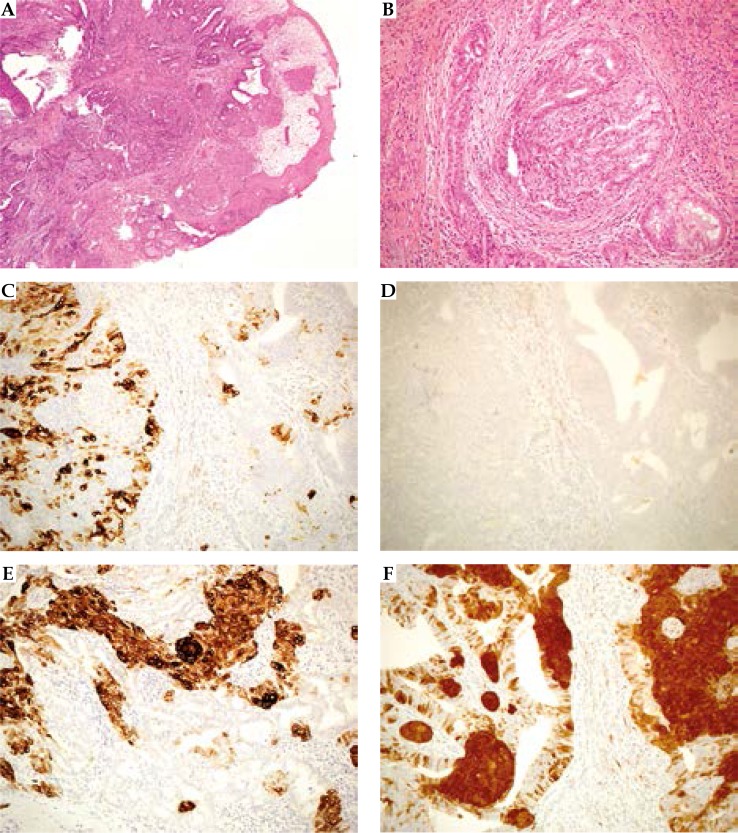
Fig. 2.
Histological imaging. A) A lobulated, pushing infiltrative neoplasm, overlined by squamous epithelium (hematoxylin/ eosin; 40×). B) The neoplasm appear constituted by two, intermingled cell populations one with squamous features, the latter with apocrine feature. The epithelial-stromal junction show aspect of desmoplasia suggestive for pushing infiltration (hematoxylin/ eosin; 200×). C) CK7 positivity in apocrine elements (IHC; 200×). D) No stain for CK20 (IHC; 200×). E) CK34βE12 positivity in squamous and myoepithelial elements (IHC; 200×). F) Diffuse and intense stain for p16 in squamous and myoepithelial elements, scattered positivity in apocrine elements (IHC; 200×)