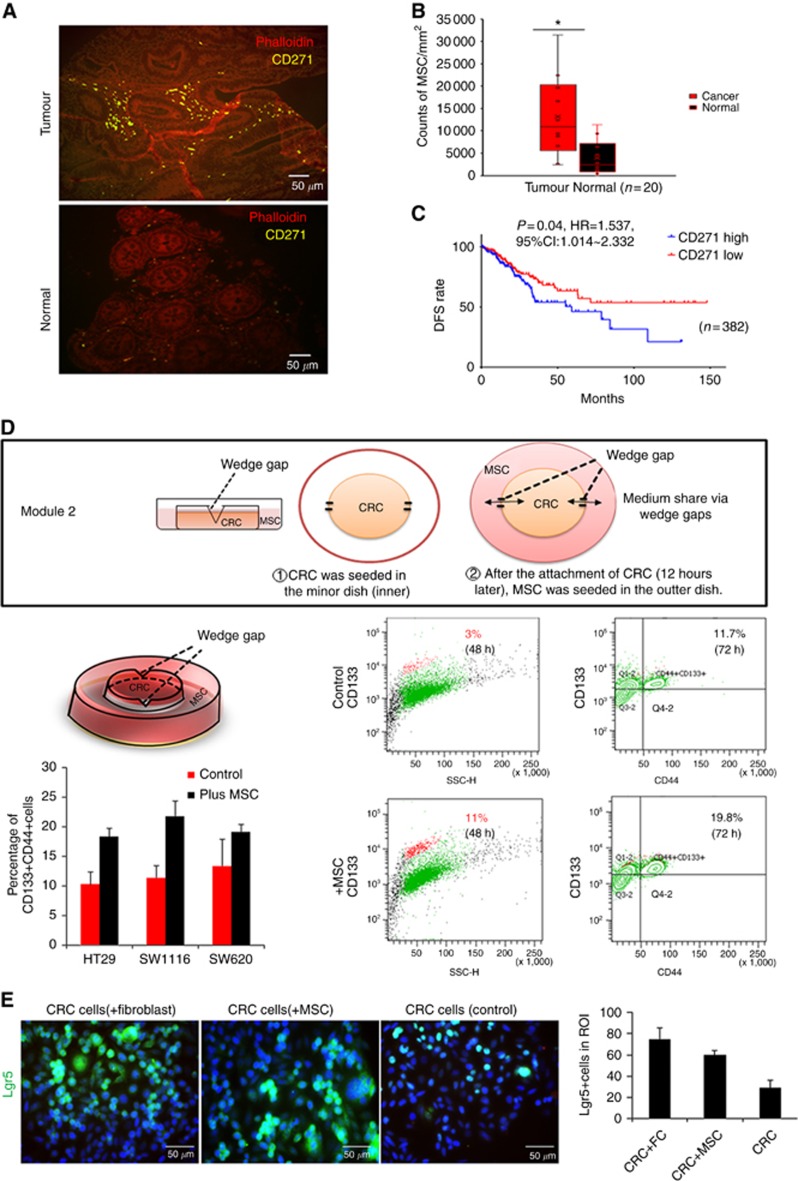
Figure 1.
Co-cultivation with MSCs promoted colorectal cancer cells (CRC) to obtain stemness in vitro. (A) Human colorectal cancer tissues and adjacent normal tissues were stained with the anti-CD271 antibody (MSCs marker, yellow). MSCs could be found surrounding the tumour lesions (200x). (B) Counts of CD271+MSCs of the slides were calculated respectively using ImageJ. MSCs were enriched in tumour site (Red box) compared with normal tissues (black box). (C) Disease-free survival (DFS) rate was analysed basing on TCGA data set. Patients were separated into CD271 mRNA z-score high and low groups. (D) Co-cultivation model for MSCs and CRC. The 3.5 cm and 10 cm dish share medium through two wedge gaps when the medium is enough to reach the level of the wedge gap. If the medium did not reach the wedge gap level, cells in two dishes could grow independently. FACS analysis of CD133+CRC stem cell-like cells, CD133+CD44+ stem cell-like cells before and after co-cultivation with MSCs. Three cell lines HT29, SW1116, and SW620 were taken into consideration. (E) Immunofluorescence staining and quantification showed the proportion of LGR5+CRC stem cell-like cells increased after co-cultured with fibroblast or mesenchymal stromal cells compared with control group. *P<0.05.