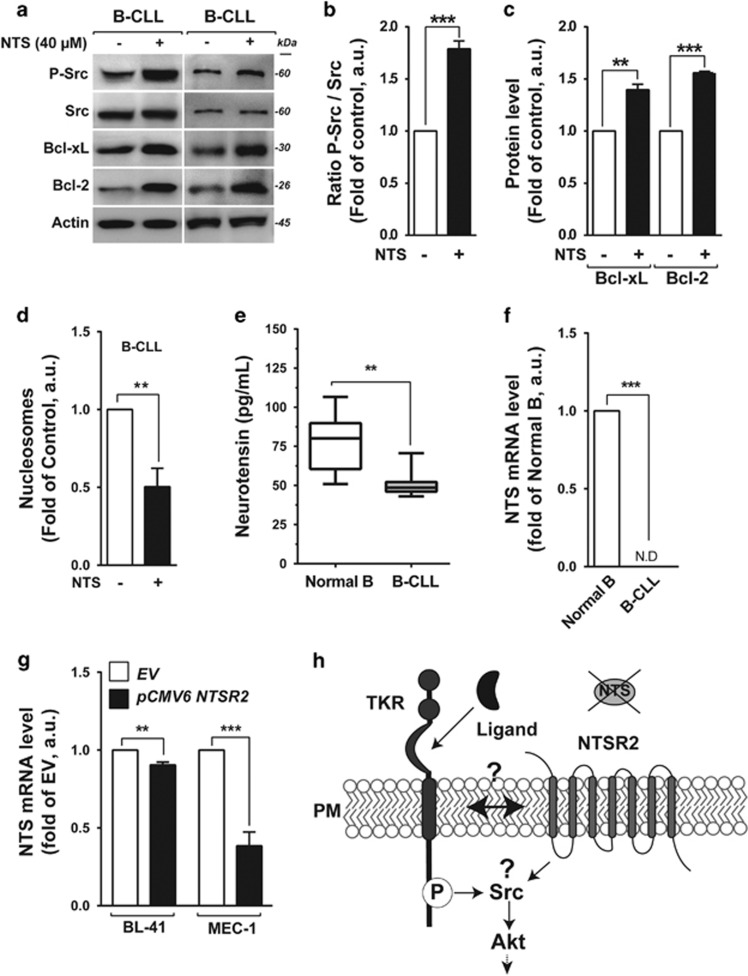
Figure 4.
Exogenous neurotensin (NTS) maintains cell survival pathways in B-CLL. (a) Representative western blot of p-Src, Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 expression in B-CLL cells after addition of neurotensin (40 μM) for 24 h. (b,c) Expression levels of P-Src (b), Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 (c) represented as, respectively, the ratio of phosphorylated Src vs pan-Src protein and the ratios of Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 to actin. Values are means±s.e.m. of B-CLL, expressed in a.u. (n=3). (d) Apoptotic ratio in B-CLL in the presence or absence of 40 μM NTS for 24 h, assessed by cell death ELISA. Values are proportions of apoptotic cells (±s.e.m.) in three independent experiments from different patients (n=3). (e) Neurotensin concentration, quantified by ELISA, from B-CLL patient plasma (n=22, gray boxes), in comparison with healthy donor plasma (n=8, white boxes). (f) Quantitative analysis of NTS mRNA level in normal B cells (n=15) and B-CLL (n=30). Data are expressed as mean fold change in expression (±s.e.m.) in comparison with normal B cells. ND: not detectable. (g) Quantitative analysis of NTS mRNA level in BL-41 or MEC-1 transfected with either NTSR2 expression vector (pCMV6 NTSR2) or empty vector (EV). Data are expressed as mean fold change (±s.e.m.) vs empty vector. (h) Schematic representation of hypothetical NTSR2 activation dependent on recruitment of a tyrosine kinase receptor (TKR). Significant P-values are indicated in the graphs **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.