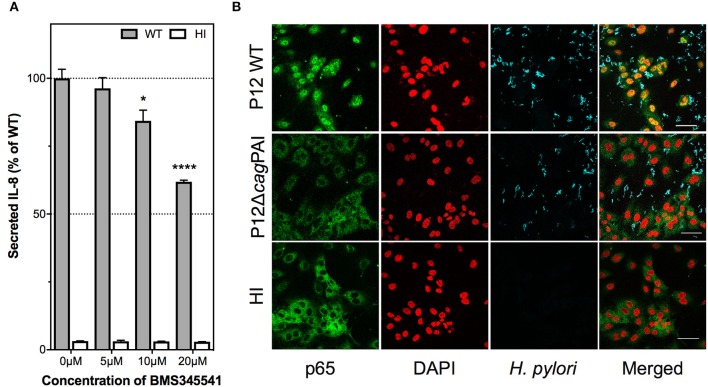
Figure 7.
Contribution of NF-κB activation to H. pylori–induced IL-8 secretion by human endothelial cells. (A) IL-8 induction is dependent upon NF-κB activation. HUVECs were pre-treated with BMS345541 at 5, 10, or 20 μM prior to inoculation with HI or H. pylori P12. Spent culture media was harvested at 24 hpi and assayed by ELISA for secreted IL-8; IL-8 levels are expressed as the mean percentage of that determined with P12 WT-infected HUVECs. Error bars denote SEM, N = 2; statistical analysis of inhibitor dose-response by two-way ANOVA (Tukey's multiple comparisons post-test); significant differences compared to 0 μM are shown; *p < 0.05; ****p < 0.0001. (B) H. pylori activates nuclear translocation of NF-κB subunit p65 upon infection of HUVECs. HUVECs inoculated with HI broth, or H. pylori strains P12 WT or P12 cagPAI mutant (MOI = 30) were fixed at 3 hpi, and immunolabeled for NF-κB p65 (green) and H. pylori (blue); nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (red); yellow/orange in merged images denotes nuclear p65. Scale bar, 50 μm. Images shown are representative of two independent experiments.