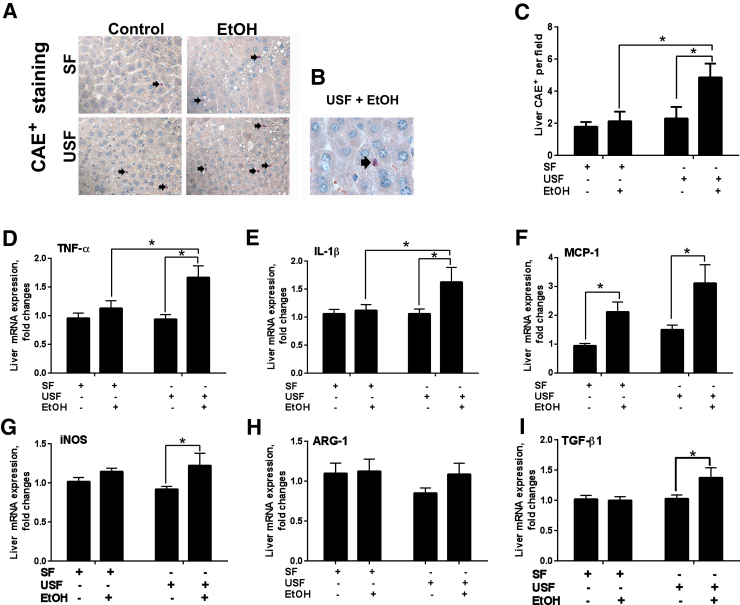
Figure 3.
Effect of different types of dietary lipids and chronic-binge–ethanol (EtOH) administration on hepatic inflammation. A and B: Representative images of chloroacetate esterase staining (CAE). Arrows indicate CAE-positive neutrophils. C: Quantification of CAE staining performed by counting CAE-positive neutrophils in a random series of five digital images per animal. D: Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). E: IL-1β. F: Monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1). G: Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). H: Arginase 1 (ARG-1). I: Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1). D–I: Hepatic mRNA levels were measured by RT-PCR. Genes were normalized to 18S rRNA as an internal control. Results are presented as fold changes relative to the SF pair-fed group. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. Each experiment is a representative or the average of 8–10 mice per group (D–I). n = 6 to 8 animals per group (C). ∗P < 0.05. Original magnification: ×400 (A); ×1000 (B). SF, saturated fat; USF, unsaturated fat.