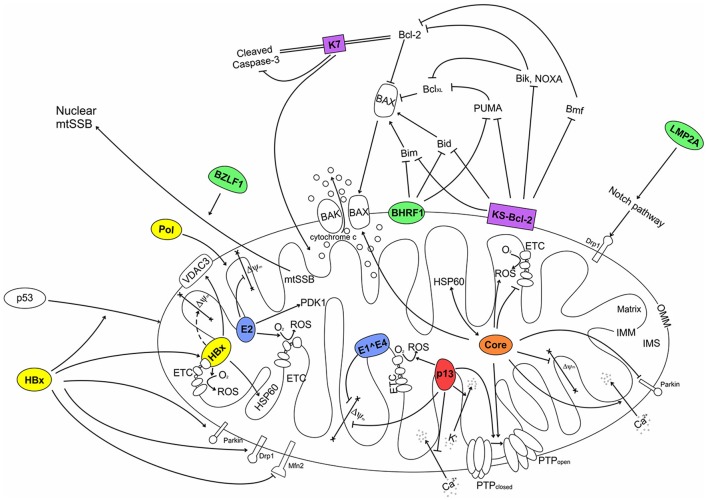
Figure 2.
Interactions of human tumor virus proteins with mitochondria. HTLV-1 (red): p13 causes an inward K+ current that leads to mitochondrial swelling, depolarization and increased ROS production that lowers the PTP opening threshold. p13 also reduces mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake. EBV (green): The Bcl-2 homolog BHRF1 localizes at the OMM and binds to Bim, Bid and PUMA, resulting in the inhibition of Bax translocation to the OMM. BZLF1 interacts with mtSSB. LMP2A increases expression of Drp1 (dynamin-related protein 1) through stimulation of the Notch pathway. KSHV (purple): The Mcl-1 homolog KS-Bcl-2 localizes at the OMM and can bind and inhibit a variety of BH3-only proteins, resulting in the inhibition of Bax-Bak oligomerization at the OMM. The K7 protein forms a bridge between cellular Bcl-2 and cleaved Caspase-3, resulting in inhibition of Caspase-3 activity. HBV (yellow): HBx interacts with the Complex IV subunit COXIII and increases ROS generation by the ETC; HBx can interact with VDAC3 and HSP60. Furthermore, HBx can induce p53 translocation to mitochondria. HBx was also shown to influence mitochondrial dynamics through its interaction with Drp1 and Mnf2. Polymerase (Pol) contains an amino-terminal MTS that determines its mitochondrial targeting; it impact on mitochondria remains to be understood. HCV (orange): Core increases mitochondrial respiration, ROS generation, and uptake of Ca2+, which sensitizes PTP opening. Core also inhibits translocation of Parkin to mitochondria, favors/facilitates/promotes Bax-Bak oligomerization, and interacts with the matrix chaperone HSP60. HPV (blue): The E2 protein interacts with IMM proteins and induce expression of the matrix protein PDK1 (pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1); E2 also increases ROS generation in mitochondria. The E1∧E4 protein causes loss of ΔΨm. OMM, outer mitochondrial membrane; IMM, inner mitochondrial membrane; IMS, inter-membrane space; ROS, reactive oxygen species; MTS, mitochondrial targeting sequence; ETC, electron transport chain; PTP, permeability transition pore; not determined.