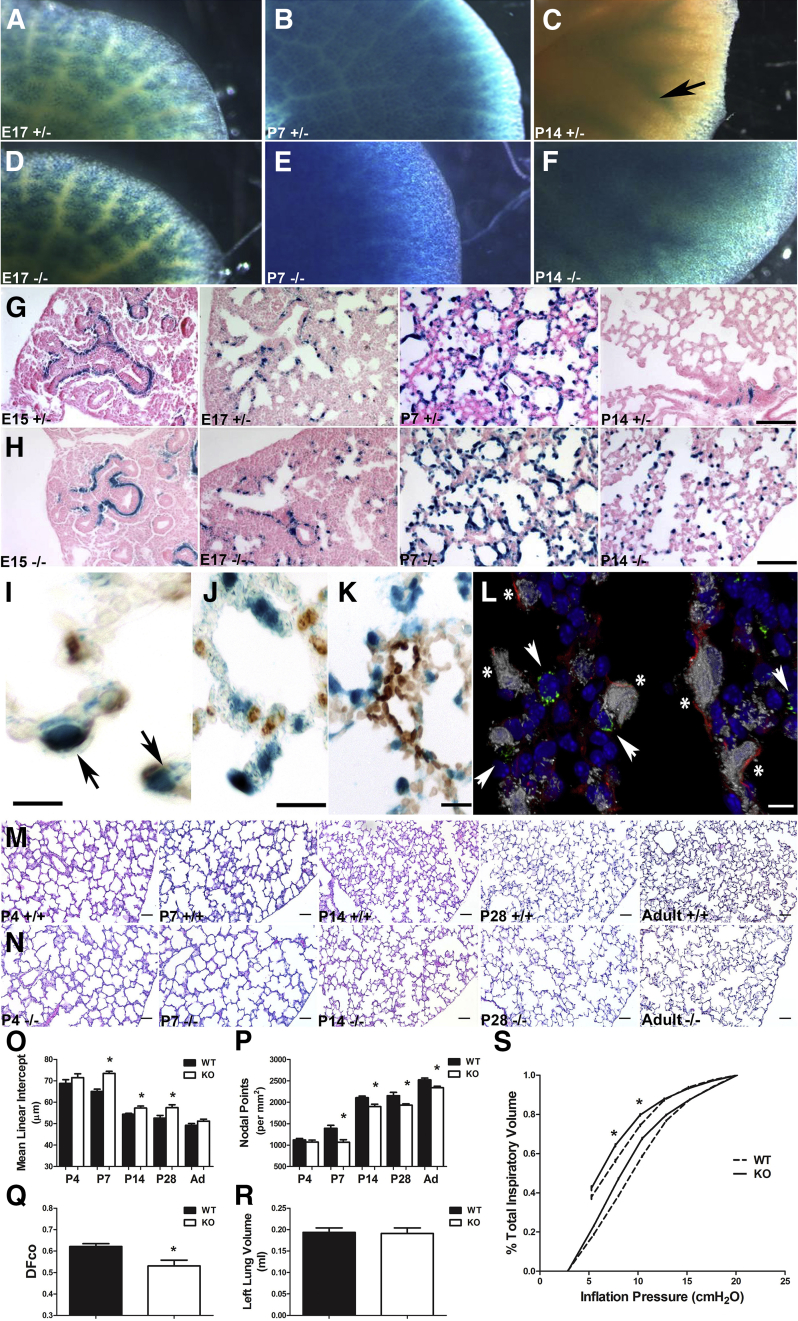
Figure 4.
Phenotypic analysis of Tgfbi knockout (KO) lungs. A–F: Whole-mount X-Gal staining indicating TgfbilacZ reporter expression in heterozygous (+/−) lungs at E17 (A), postnatal day (P) 7 (B), and P14 (arrow indicates lacZ restricted around large airways; C) compared with TgfbilacZ nulls (−/−) at E17 (D) and P7 (E) and P14 (F). F: Although there is similar lacZ spatiotemporal expression at E17 and P7, there is widespread ectopic lacZ reporter expression within the P14-null distal airspaces. G and H: Histological analysis confirms above whole-mount reporter patterns and ectopic TgfbilacZ expression in developing septal tips of P14 nulls (H) compared with heterozygous controls (G). I–K: Immunohistochemical analysis of X-Gal–stained sections demonstrates colocalization of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) protein (I, marker of alveolar myofibroblasts) with TgfbilacZ-expressing cells (arrows) but not with Pro-SPC (marker of alveolar type II cells; J) or platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM) marker (K). L: Confocal coimmunolocalization of TGFBI-driven lacZ (gray) with α-SMA (red), Pro-SPC (green), and nuclear DAPI (blue) markers. There is colocalization of lacZ with α-SMA (asterisk), but not with Pro-SPC (arrowheads). M and N: Hematoxylin and eosin–stained inflation-fixed lung sections throughout alveolar lung development in wild-type (M) and Tgfbi nulls (N) from P4 through 12 months/adulthood (Ad). O and P: Quantification of distal airspace development of sections in M and N via mean linear intercept (O) and nodal point density (P) in wild-type (WT) and Tgfbi nulls reveals that during the period of rapid alveolar septation, loss of Tgfbi retards alveolar septation, resulting in larger and/or simpler distal airspaces from P7 onwards. Q: Functional analysis by way of measurement of the diffusing factor for carbon monoxide (DFco) in adult WT and Tgfbi nulls reveals a persistent functional insufficiency. R: However, left lung volume, as assessed by water displacement in adult WT and Tgfbi nulls, is equivalent. S: Assessment of lung elastance by pressure-volume loops in adult WT (broken line) and Tgfbi nulls (solid line) confirms nulls exhibit decreased elastic recoil. Data are represented as means ± SEM (O–R). N = 4 to 9 separate animals per group per time point (A–S). ∗P < 0.05 by t-test (WT versus Tgfbi null at each time point). Scale bars: 50 μm (G, H, M, and N); 5 μm (I and L); 10 μm (J); 20 μm (K).