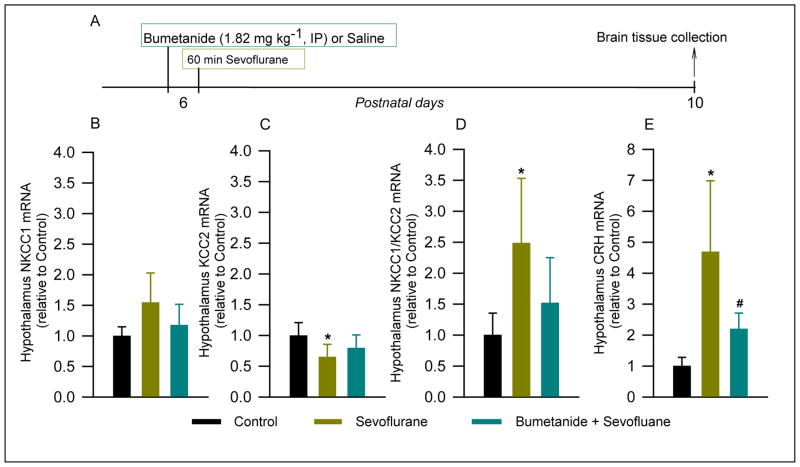
Figure 1. Anesthesia with sevoflurane of rat pups for 60 min at postnatal day (P) 6 reduced levels of K+-2Cl− (KCC2) mRNA, increased Na+-K+-2Cl− (NKCC1)/KCC2 mRNA ratio and increased levels of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) mRNA in the hypothalamus at P10. These effects were alleviated by pretreatment with bumetanide prior to anesthesia with sevoflurane.
The brain hypothalamus tissue samples were collected 4 days after the onset of anesthesia with sevoflurane for qRT-PCR analyses. (A) Illustration of the experimental protocol. Shown are the respective levels of NKCC1 mRNA (B), KCC2 mRNA (C), the resulting NKCC1/KCC2 mRNA ratios (D) and CRH mRNA (E). Data normalized against Control are means ± SD from 5–6 rats per treatment group. *P = 0.02 vs. Control; #P = 0.025 vs. Bumetanide plus Sevoflurane plus maternal separation.