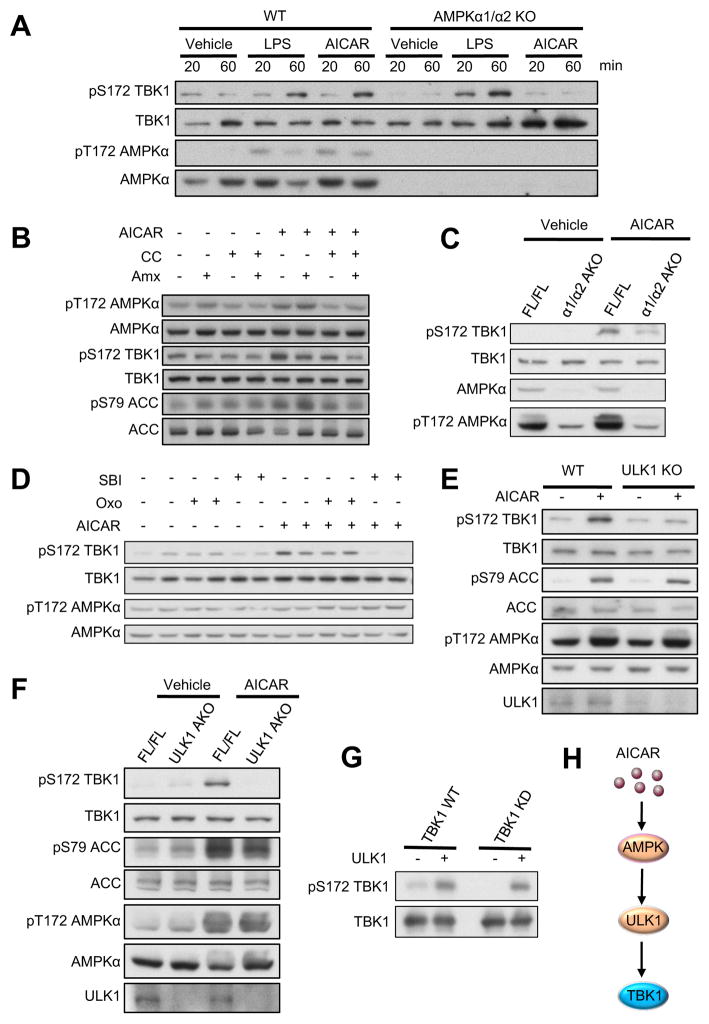
Figure 4. Activation of AMPK induces TBK1 phosphorylation via ULK1 in vitro and in vivo.
(A) IB analysis of WT and AMPKα1/α2 KO MEFs treated with Vehicle, LPS (100ng/ml) or AICAR (500μM) for indicated time. (B) IB analysis of 3T3-L1 adipocytes pretreated with Vehicle, compound C (CC, 5μM) or Amlexanox (Amx, 50μM) for 1hr, and then treated with AICAR (500μM) for 45min. (C) IB analysis of eWAT from FL/FL and α1/α2 AKO mice (12–14 weeks old) intraperitoneally injected with Vehicle or AICAR (500mg/kg) for 45min. (D) IB analysis of 3T3-L1 adipocytes pretreated with Vehicle, Oxozeaenol (Oxo, 300nM) or SBI- 0206965 (SBI, 10μM) for 1hr, and then treated with AICAR (500μM) for 45min. (E) IB analysis of WT and ULK1 KO MEFs treated with Vehicle or AICAR (500μM) for 45min. (F) IB analysis of eWAT from FL/FL and ULK1 AKO mice (12–14 weeks old) intraperitoneally injected with Vehicle or AICAR (500mg/kg) for 45min. (G) IB of in vitro kinase assay with ULK1 active kinase and immunoprecipitated Flag-TBK1 WT or Flag-TBK1 KD. Immunoprecipitated Flag- TBK1 WT were pretreated with lambda-protein phosphatase before performing kinase assay. Each panel is a representative experiment that was repeated three times. (H) Proposed model of AMPK-induced activation of TBK1. See also Figure S4.