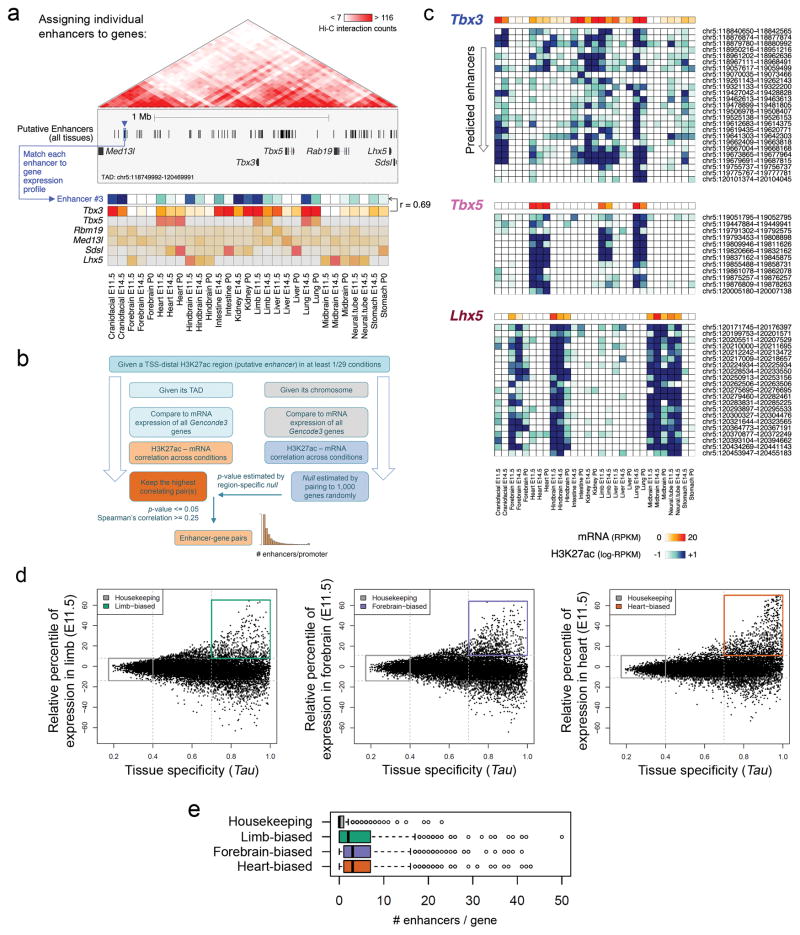
Extended Data Figure 9. A correlative framework to define enhancer-promoter associations across the mouse genome.
(a) The TAD including the transcriptional regulators Tbx3, Tbx5 and Lhx5 illustrates the statistical framework to define enhancer-promoter associations genome-wide. For each predicted enhancer, correlation between its H3K27ac signal (blue arrowhead, blue-shades heat map) with the mRNA expression profiles of every gene in the TAD (red-shades heat map) across all available tissues and developmental stages was assessed. The enhancer was then assigned to the most highly correlated gene, Tbx3 in the case of Enhancer #3. (b) Schematic depicting the underlying statistical framework used to determine genome-wide enhancer-promoter interactions (see Methods for a detailed description). (c) Activity pattern for the enhancers assigned to Tbx3, Tbx5 and Lhx5 genes. Genomic coordinates are listed on the right. For each predicted enhancer-gene pairing, Spearman’s Correlation Coefficient (SCC, n = 29) and the corresponding empirically estimated p-value (from 1,000 random enhancer-gene pairings) are shown in Supplementary Table 11. (d) Identifying genes with biased expression in embryonic limb, forebrain, or heart. Expression variability across 29 RNA-seq datasets from multiple tissues and developmental time points, measures of tissue specificity (Tau, x-axis) and specific tissue-biased expression at E11.5 (y-axis) for each protein-coding gene were calculated (see Methods for additional details). Housekeeping genes were defined as displaying Tau <= 0.4 and relative expression in the limb between the 5th and 95th percentiles. Tissue-biased genes were defined as showing Tau >= 0.7 and relative expression higher than the 95th percentile. (d) Distribution of enhancer numbers assigned to each gene, for the different gene categories. Genes with tissue-biased expression profiles were associated with a significantly higher number of enhancers than housekeeping genes. P = 4e-121 (n=553), P = 7e-97 (n=626) and P = 6e-83 (n=826) for limb, forebrain and heart biased genes, respectively (two sided Mann-Whitney tests). n = 1,287 for housekeeping genes. Box plots indicate median, interquartile values and range. Outliers are shown as individual points.