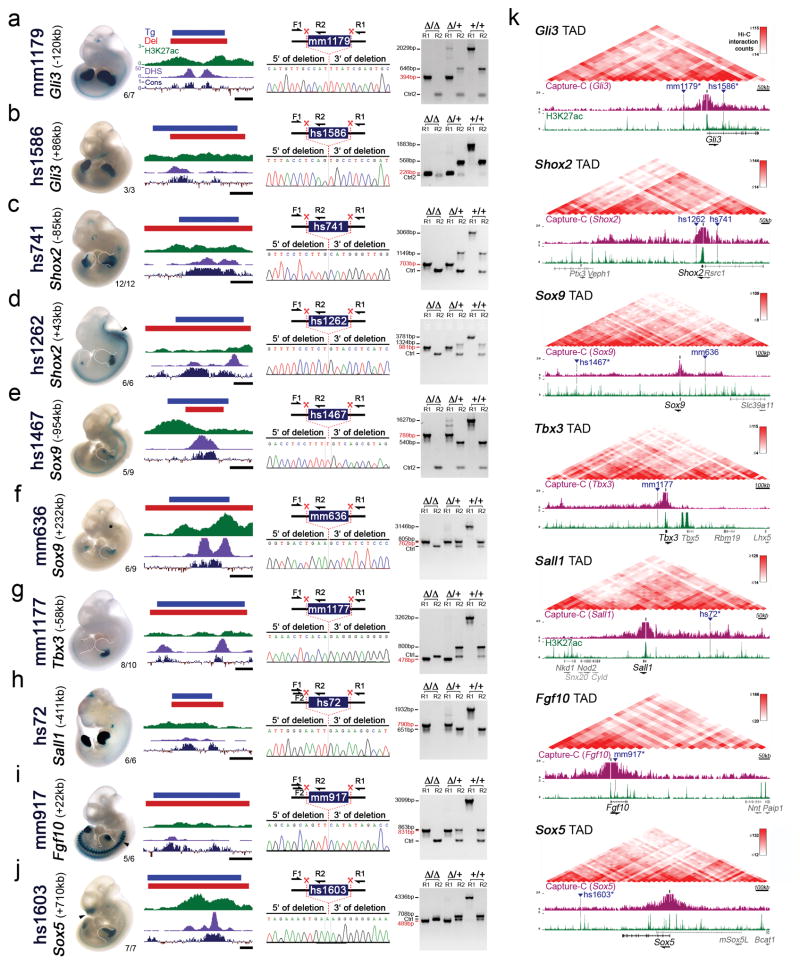
Extended Data Figure 1. CRISPR-deletion of ten limb enhancers and regulatory interaction landscape of associated target genes.
(a–j) Left panels: Representative activity patterns of the selected enhancers in mouse embryos at E11.5 (VISTA enhancer browser)13 and the respective genomic enhancer region (Tg, blue bar) along with the region deleted in enhancer knockout mice (Del, red bar). Corresponding H3K27 acetylation patterns (green) in wild-type mouse embryonic forelimbs at E11.5 (this study) are depicted with open chromatin (ENCODE DHS in forelimbs at E11.5, purple) and the Placental Mammal basewise conservation track by PhyloP (Cons, blue/red). Scale bars, 500 bp. VISTA enhancer IDs (mm and hs numbers) are indicated on the left, with the distance of the enhancer from the transcriptional start site of the predicted target gene in the mouse genome. Numbers in the bottom right of each embryo indicate reproducibility of enhancer reporter assay. Arrowheads mark additional activity domains (other than limb): hs1262 (hindbrain, reproducibility: 5/6, also shown previously17), mm917 (dorsal root ganglion, 7/7) and hs1603 (nose, 7/7; and branchial arch, 5/7). Asterisk indicates potential craniofacial enhancer activity for mm636, which was observed in 3/9 embryos64. Right panels: PCR validation strategy and results for enhancer KO lines. Red scissors indicate CRISPR-mediated deletion breakpoints. PCR was used to detect the wild-type (+) and enhancer deletion (Δ) alleles. Below, Sanger sequencing traces show the deletion breakpoints (indicated by the dashed line) for the enhancer KO alleles. PCR genotyping results are shown with amplicon sizes indicated on the left (enhancer deletion allele in red). Primers (Ctrl or Ctrl2) amplifying an unrelated genomic region were included as a PCR positive control. See Supplementary Table 3 for all primer sequences and related PCR product sizes. (k) Top: Hi-C interaction heatmaps of topologically associated chromatin domains (mESC TADs)26. Bottom: Selected enhancers (blue triangles) and their predicted target genes (TSS indicated as black bar). The Capture-C UCSC browser track (purple) illustrates three-dimensional chromatin interaction profiles from E11.5 embryonic limbs (3kb window) using promoters of the predicted enhancer target genes as viewpoints22. H3K27ac enrichment (green) in wildtype forelimbs at E11.5 (this study) is shown below. Six of the ten enhancers selected for deletion analysis display local Capture-C enrichment (marked by “*”), indicating physical interaction with the predicted target gene promoter at E10.5 or E11.5, based on the stringent statistical approach (95th percentile threshold) applied in the original study22. Other genes present in the TAD are shown in gray.