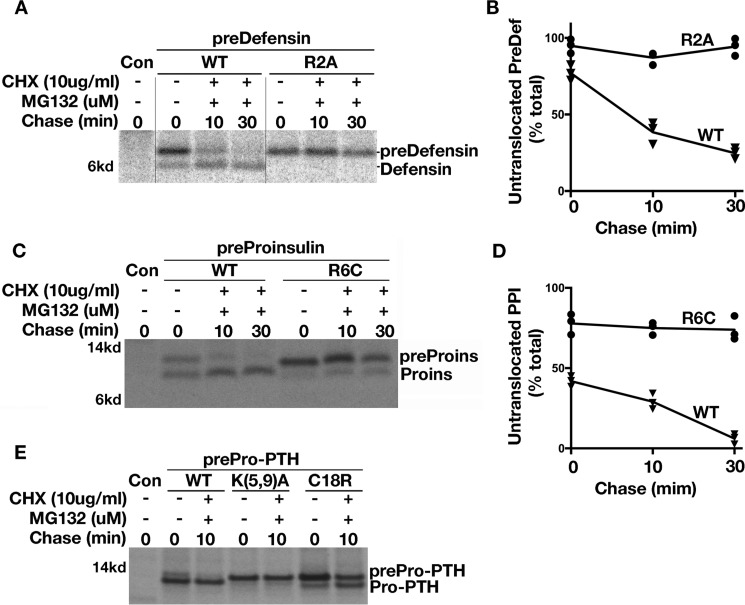
Figure 4.
Loss of positive charge in the n-region of SP impairs post-translational translocation of small secretory preproteins. A, 293T cells transfected with plasmids encoding predefensin-WT or n-region mutant R2A were labeled for 5 min followed by 0, 10, or 30 min of chase in the presence of 10 μm MG132 and 10 μg/ml CHX. Post-translational translocation of predefensin-WT and mutant were analyzed in 4–12% NuPAGE gel. B, newly synthesized signal-uncleaved and -cleaved predefensin-WT and R2A from three experiments were quantified using ImageJ. The percentages of signal-uncleaved predefensin-WT and R2A at 0-, 10-, or 30-min chase time points were calculated and shown. C, 293T cells transfected with plasmids encoding preproinsulin-WT or R6C were labeled for 5 min followed by a 0-, 10-, or 30-min chase in the presence of 10 μm MG132 and 10 μg/ml CHX. Post-translational translocation of preproinsulin-WT and R6C were analyzed in 4–12% NuPAGE gel. D, newly synthesized signal-uncleaved and -cleaved preproinsulin-WT and R2A from three experiments were quantified using ImageJ. The percentages of signal-uncleaved preproinsulin-WT and R6C at a 0-, 10-, or 30-min chase time points were calculated and shown. E, 293T cells transfected with plasmids encoding prepro-PTH wildtype (WT), n-region mutant K5A/K9A, or h-region mutant C18R were labeled for 5 min followed by a 0- and 10-min chase in the presence of 10 μm MG132 and 10 μg/ml CHX. Untranslocated but fully synthesized WT predefensin, preproinsulin, and prepro-PTH could clearly undergo post-translational translocation and were further processed during the 10–30-min chase. However, post-translational translocation of all three SP n-region mutants were essentially blocked. By contrast, the mutation in the h-region of prepro-PTH C18R could undergo post-translational translocation during a 10-min chase.