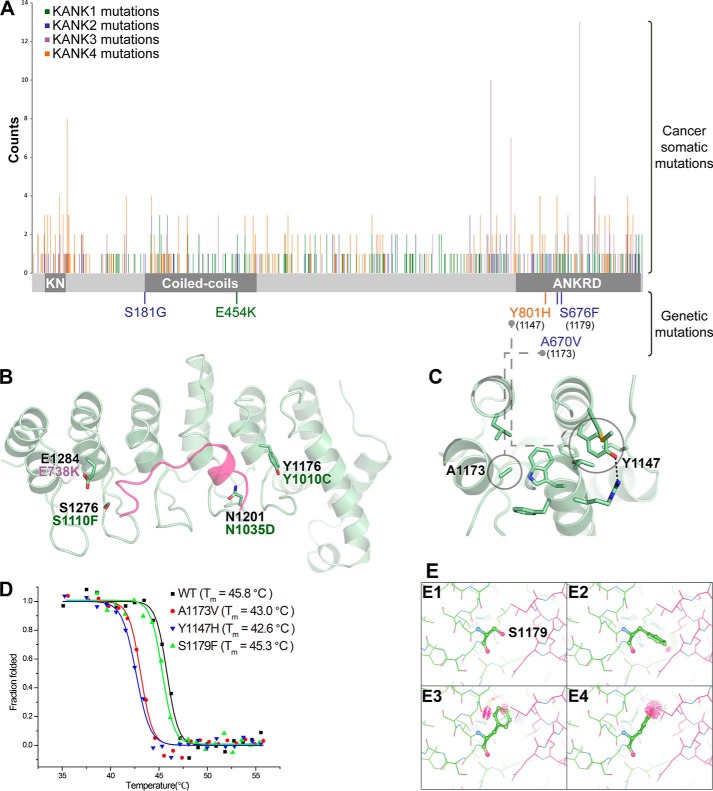
Figure 7.
Disease-related mutations in KANK family members. A, distribution of cancer somatic and genetic mutations in KANKs, including missense, nonsense, deletion, or insertion mutations, which result in changes of protein products. The columns indicate the mutation positions and their reported times according to the COSMIC database (http://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/cancergenome/projects/cosmic/).5 The schematic domain organization is indicated for reference. KN, N-terminal 30-residue motif. B, four somatic mutation sites are mapped to the KANK1_ANKRD structure. The corresponding mutations are also indicated. C, two disease-causing mutation sites are located in the hydrophobic core of KANK1_ANKRD, including the mutations identified in patients with nephrotic syndrome or keratoderma. D, thermal denaturation curves of the wildtype KANK1_ANKRD and its mutants were measured using CD spectroscopy at 222 nm. E, analysis of potential steric clashes in the KANK1_ANKRD-KIF21A_H complex for Ser-1179KANK1 (E1) and three potential side-chain rotamers of the S1179F mutation (E2–E4).