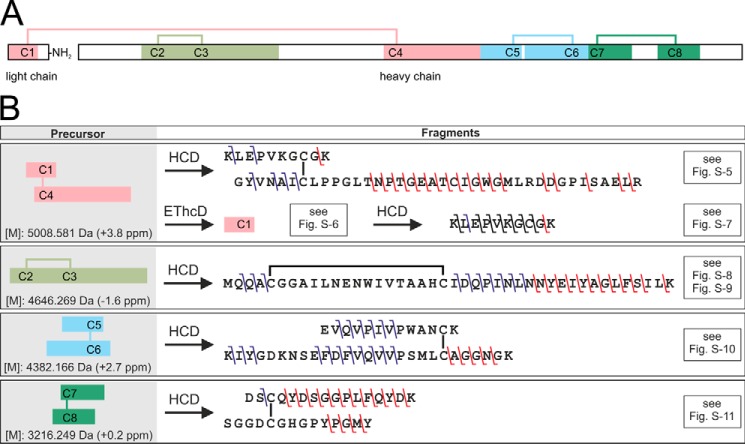
Figure 4.
Disulfide bridge pattern of the PQM protease and overview on its elucidation. A, overview of the heterodimeric structure of the isolated protease. The light chain is C-terminally amidated. Disulfide bridges are shown as lines. Colored fragments represent cysteine-connected tryptic peptides detected by LC-MS of the digested, non-reduced PQM protease. B, overview of identified b- and y-fragment ions in the MS2 and MS3 spectra of the cysteine-connected tryptic peptides. The used fragmentation methods, higher-energy collisional dissociation (HCD), and electron transfer/higher-energy collision dissociation (EThcD) are abbreviated. Precursor masses are given as monoisotopic uncharged. The deviation of the experimental from the theoretic masses is given in brackets. Relevant mass spectra and tables of identified fragment ions are available in Fig. S5–S11 and Tables S4–S8.