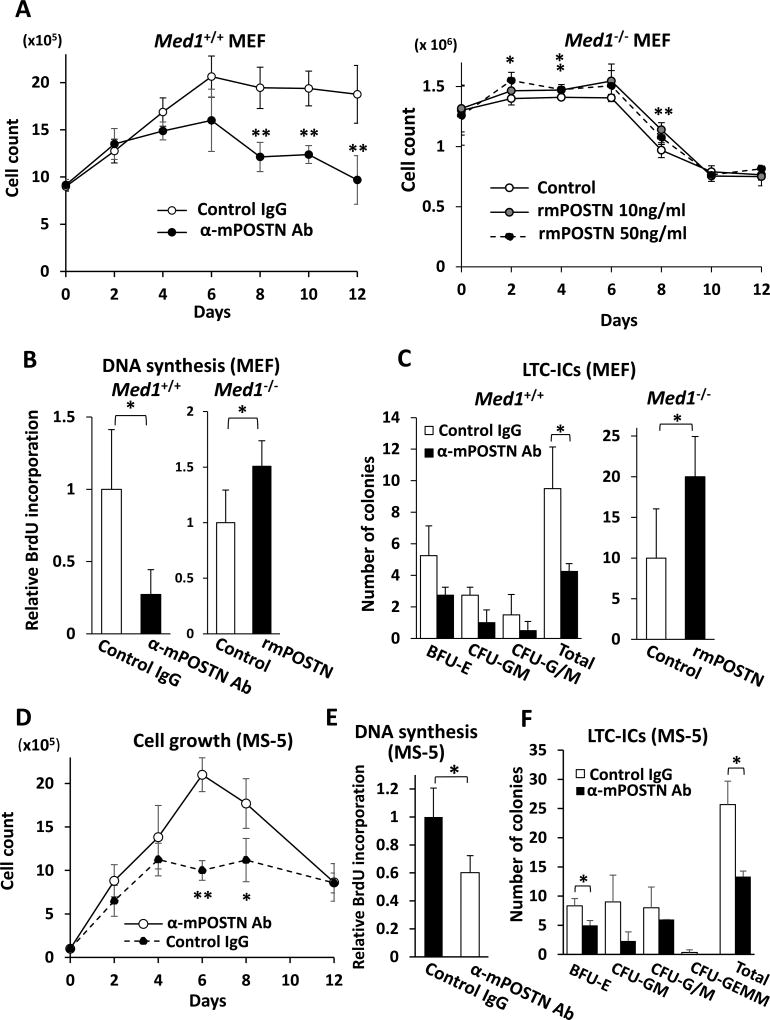
Fig. 1. POSTN promotes BM cell growth and HPCs support on MEFs and MS5 BM stromal cells.
(A) The number of BM cells, when cocultured on Med1+/+ MEFs, decreased in the presence of anti-mPOSTN Ab (left panel) and, when cocultured on Med1−/− MEFs, slightly increased in the presence of rmPOSTN. α, anti.
(B) DNA synthesis of BM cells, measured by BrdU incorporation, on Med1+/+ MEFs decreased in the presence of anti-mPOSTN Ab (left panel) and, on Med1−/− MEFs, increased in the presence of 10 ng/ml rmPOSTN.
(C) HSPCs support was quantitated by LTC-ICs. On Med1+/+ MEFs, the number of colonies decreased in the presence of anti-mPOSTN Ab (left panel) and, on Med1−/− MEFs, total LTC-ICs increased in the presence of 10 ng/ml rmPOSTN (right panel).
(D, E) The number (D) and DNA synthesis (E) of BM cells, when cocultured with MS-5 cells, decreased in the presence of anti-mPOSTN Ab.
(F) The number of LTC-ICs, when BM cells were cocultured with MS-5 cell, decreased in the presence of anti-mPOSTN Ab.
N = 4 (A–F).