Figure 4. CE2 is necessary for Hsp70 to bind to Hsf1.
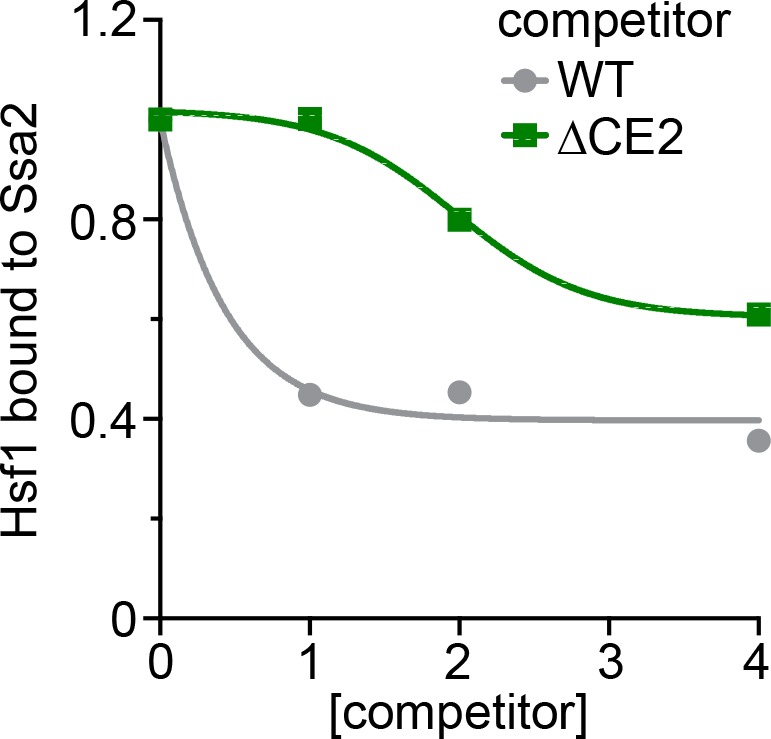
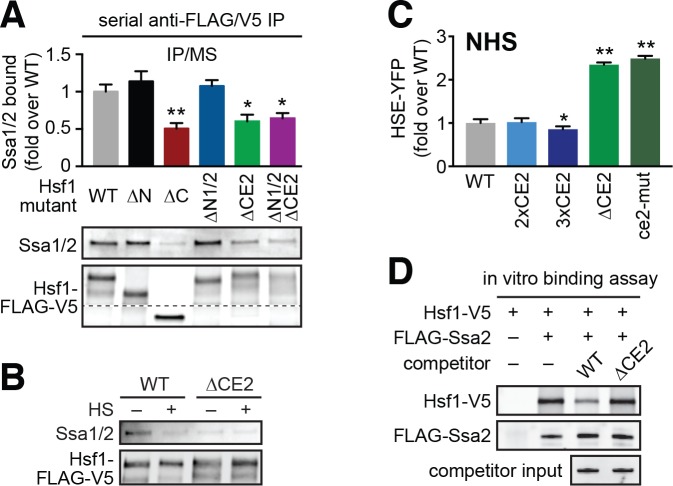
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation of Hsf1 and Hsp70. The indicated Hsf1 mutants, C-terminally tagged with 3xFLAG-V5, were serially precipitated and subjected to mass spectrometry as described. The ratio of Hsp70 (Ssa1/2) to Hsf1 was determined in three biological replicates (bar graph, error bars are the standard deviation). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA (*p<0.05; **p<0.01). An additional replicate was analyzed by Western blot using antibodies against Ssa1/2 and the FLAG tag to recognize Hsf1. The FLAG blot was cropped in the middle to show the much smaller Hsf1∆C. The immunoblot results are not as quantitative as MS and therefore were not used in generating bar graph. (B) Cells expressing C-terminally 3xFLAG-V5-tagged wild type Hsf1 and Hsf1∆CE2 were either left untreated or heat shocked for 5 min at 39°C before serial Hsf1 immunoprecipitation and analyzed by Western blot using antibodies against Ssa1/2 and the FLAG tag to recognize Hsf1. (C) Cells expressing the indicated mutants of Hsf1, expressed as the only copy of Hsf1, were assayed for HSE-YFP levels under non-heat shock conditions by flow cytometry. The error bars are the standard deviation of three replicates. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA (*p<0.05; **p<0.01). (D) In vitro Hsf1:Hsp70 binding assay. Recombinant Hsf1-V5 and 3xFLAG-Ssa2 were purified, incubated together and assayed for binding by anti-FLAG immunoprecipitation followed by epitope-tag-specific Western blot. Addition of 5-fold molar excess of wild type Hsf1-6xHIS but not Hsf1∆CE2-6xHIS diminished the amount of Hsf1-V5 bound to 3xFLAG-Ssa2.
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Titration series of the in vitro Hsf1:Hsp70 binding competition assay.