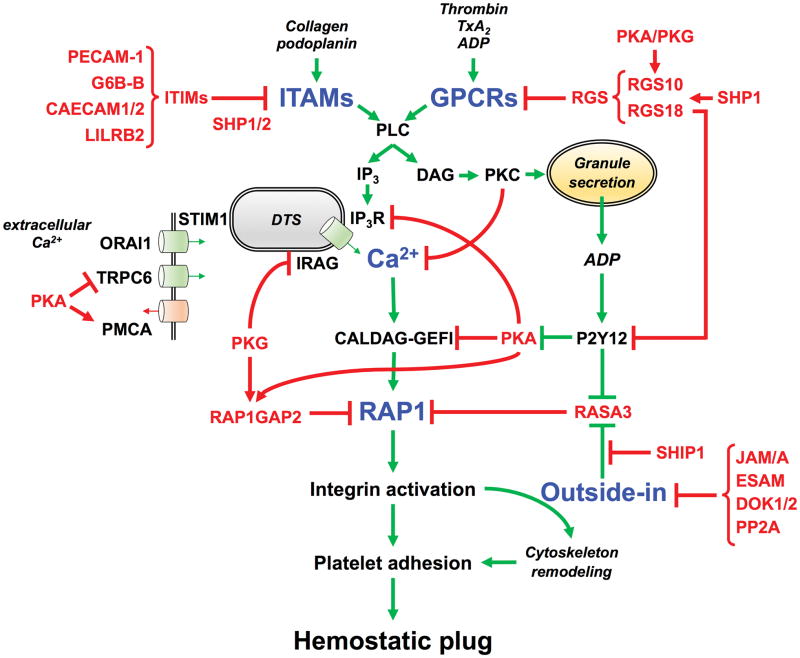
Figure 2. Negative regulators that control platelet activation and adhesiveness.
The tight balance between inhibitory (red arrows) and activatory (green arrows) signaling pathways is critical to maintain patrolling platelets in a quiescent, non-adhesive state and/or to limit platelet adhesion to sites of injury. This schematic figure shows the critical signaling nodes (blue) where the positive and negative signals are integrated to finely control platelet activation and adhesiveness in space and time, most importantly at the level of 1) receptor stimulation, 2) intracellular Ca2+ elevation, 3) Rap1 activation, and 4) outside-in signaling. The regulatory elements that provide important negative feedback at these critical checkpoints of the activation process are labelled in red. Abbreviations: ITAMs (immune receptor tyrosine-based activation motif), ITIMs (Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Inhibition Motif), PECAM-1 (Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-1, CD31), G6B-B (Megakaryocyte and Platelet Inhibitory Receptor), CAECAM1/2 (Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1/2), LILRB2 (Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 2), GPCRs (G protein-coupled receptors), RGS (Regulators of G-protein Signaling), TxA2 (thromboxane A2), PLC (phospholipase C), IP3 (inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate), DTS (dense tubular system), Ca2+ (calcium ions), IP3R (IP3 receptor), IRAG (IP3R-associated cGMP kinase substrate), STIM1 (Stromal interaction molecule 1), ORAI1 (Calcium Release-Activated Calcium Modulator 1), TRPC6 (Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 6), PMCA (plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase), DAG (diacylglycerol), RAP1 (Ras-proximate-1), CALDAG-GEFI (Ca2+-regulated guanine nucleotide exchange factor), PKC (protein kinase C), ADP (adenosine diphosphate), PKA (protein kinase A), PKG (protein kinase G), P2Y12 (G-protein coupled purinergic receptor), RASA3 (RAS p21 protein Activator 3), RAP1GAP2 (RAP1 GTPase activating protein 2), SHIP1 (phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate 5-phosphatase 1), SHP1/2 (Src-homology 2 domain (SH2)-protein tyrosine phosphatase), JAM/A (Junctional adhesion molecule-A), ESAM (Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule), DOK1/2 (Docking protein 1/2), PP2A (Protein phosphatase 2A).