Figure 9.
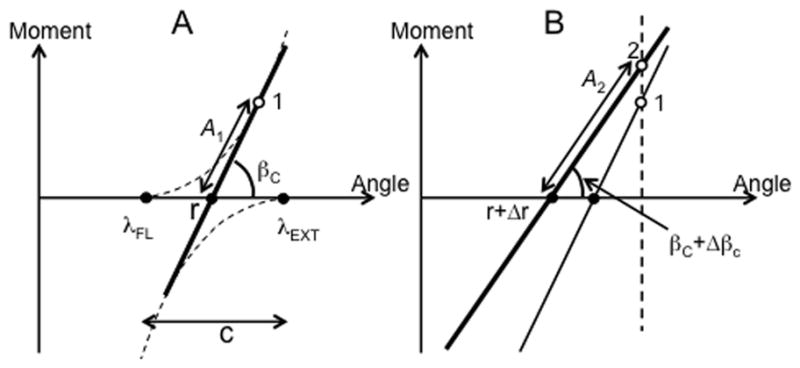
A: The control of a joint crossed by only two muscles, flexor and extensor, can be described with setting two values of λ, {λFL; λEXT} or an equivalent pair of variables, r-command and c-command. The r-command sets the intercept of the torque-length line with the length axis and the c-command defines the slope of that line. Projection of the multi-dimensional afferent space on the torque-length line may be expressed as a value A1 of a higher-order variable A. B: When a person presses against a stop r-command shifts by Δr and βc shifts by Δβc. The value of A changes to A2.
