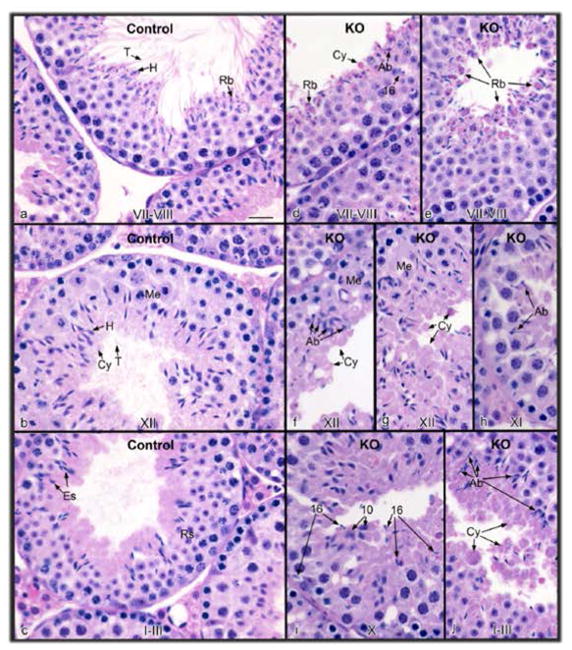
Figure 5. Histology of the testis from control (a–c) and conditional Ift140 knockout (KO) mice (d–j).
The stage of spermatogenesis is identified at the bottom of each figure. (a) Control stage late VII–VIII, showing normal step 16 elongated spermatids with long tails (T) extending into the lumen and heads (H) surrounded by forming residual bodies (Rb). (b) Control stage XII, showing spermatocytes in meiotic division (Me), step 12 elongating spermatids with heads (H) of condensed chromatin, bulges of cytoplasm (Cy) and tails extended into the lumen. (c) Control stage I–III, showing elongated spermatids (Es) with tails extending into the lumen and heads extending toward the round spermatids (Rs). (d) KO stage VII–VIII, showing failure of spermiation of step 16 spermatids that were retained in the epithelium, and accumulation of residual bodies (Rb) and cytoplasmic bodies (Cy) at the lumen. Abnormally shaped spermatid heads (Ab) are also present. (e) KO stage VII–VIII, showing the release of residual bodies (Rb) into the lumen, with some attached spermatid heads. (f) KO stage XII, showing accumulation of abnormal spermatids (Ab), with cytoplasm (Cy) extending into the lumen without the formation of tails. Spermatocytes in meiotic division (Me) appear normal. (g) KO stage XII, showing excess spermatid cytoplasm (Cy) being released into the lumen. Me, meiotic division. (h) KO stage XI, showing abnormal (Ab) elongated spermatid heads. (i) KO stage X, showing step 16 elongated spermatids mixed among step 10 spermatids, due to failure of spermiation in stage VIII. (j) KO stage I–III, showing the accumulation of spermatid cytoplasm bodies in the lumen (Cy), with some attached spermatid heads. Abnormally shaped spermatid heads (Ab) are also found lining the lumen. Bar = 20 μm for all photos.