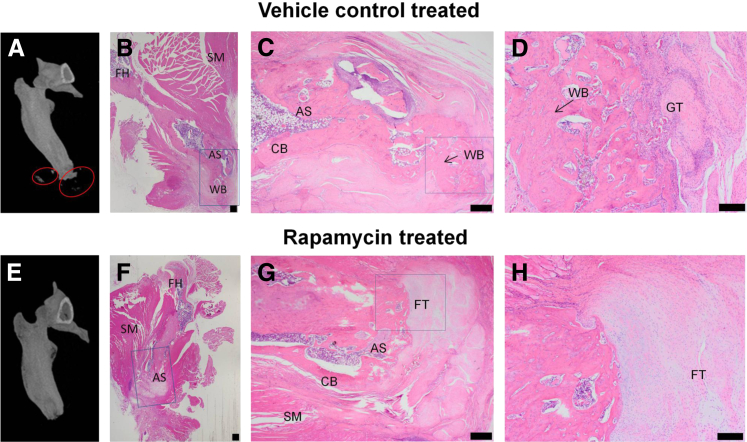
Figure 2.
Rapamycin treatment attenuates the formation of ectopic bone in the blast-related extremity injury/methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection model of heterotopic ossification (HO). A and E: Representative three-dimensional–rendered micro-computed tomography images of rat femurs at postoperative day 84 treated with vehicle control (3% dimethyl sulfoxide/saline; A) or rapamycin (2.5 mg/kg per day for 14 days, i.p; E). Areas of HO formation (red circles). B–D and F–H: Histologic assessment of hematoxylin and eosin–stained tissue sections from animals treated with vehicle control (B–D) and rapamycin (F–H). Areas of interest in near the distal end of the residual femur (boxed areas) in B, C, F, and G were examined at higher magnification and are shown in C, D, G, and H, respectively. Scale bars: 500 μm (B, C, F, and G); 200 μm (D and H). AS, amputation site; CB, cortical bone; FH, femoral head; FT, fibroblastic tissue; GT, granulation tissue; SM, skeletal muscle; WB, woven bone.