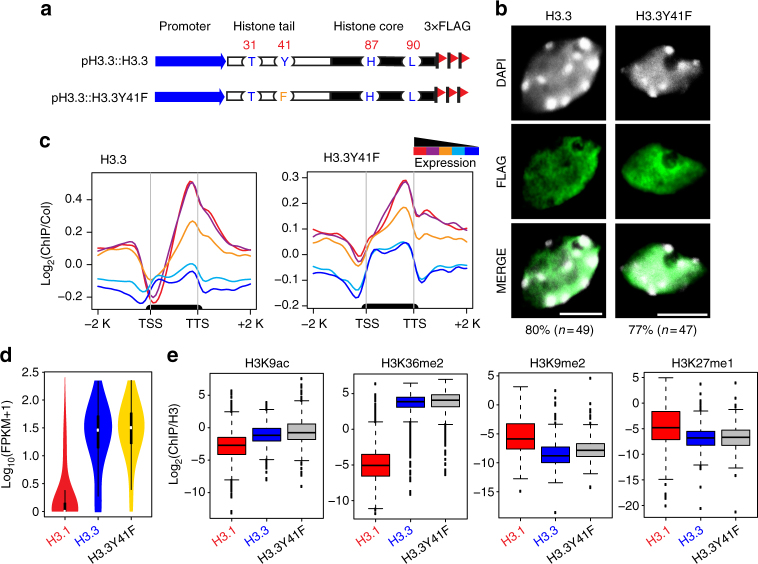
Fig. 2.
Tyr41 is dispensable for H3.3 genomic distribution. a Schematic diagram of wild-type H3.3 and H3.3Y41F FLAG-tagged constructs. b Localization of wild-type H3.3 and H3.3Y41F protein in nuclei (bar = 5 μm). The n represents the total number of examined nuclei. The percentage describes the ratio of the nuclei showing the H3 distribution pattern out of total examined nuclei. DAPI indicates the DAPI staining of the nucleus. c Metagene plots of wild-type H3.3 and H3.3Y41F ChIP-seq reads over five groups of genes divided based on their expression levels. The black bar in the x-axis represents genes. TSS, transcription start sites; TTS, transcription terminal sites; −2 K and +2 K represent 2 kb upstream of TSS and 2 kb downstream of TTS, respectively. The y-axis represents the log2 value of H3.3 and H3.3Y41F ChIP-seq reads normalized to those of Col-0. d Violin plot showing the expression levels of genes associated with H3.1, H3.3, and H3.3Y41F ChIP-seq peaks. The y-axis represents the log10 value of FPKM +1. FPKM, fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads. RNA-seq data were from 3-week-old seedlings. e Boxplots of histone modification levels over ChIP-seq peaks of H3.1, H3.3, and H3.3Y41F. The y-axis represents the ChIP-seq read density normalized by H3. Histone modification ChIP-seq data were from 2-week-old aerial tissues