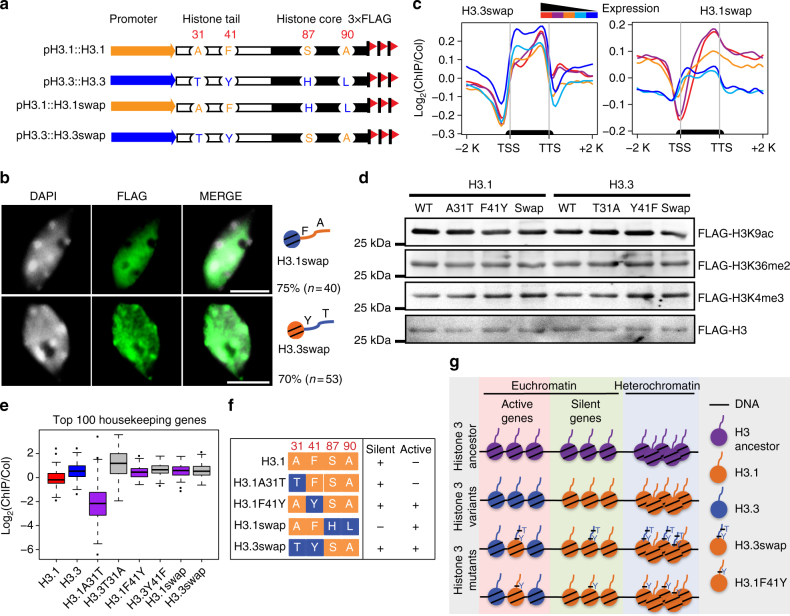
Fig. 5.
Phe41 coordinates with the histone core region to determine H3.1 distribution pattern. a Schematic diagram of H3.1, H3.3, H3.1swap, and H3.3swap FLAG-tagged constructs. b Localization of H3.1swap and H3.3swap protein in nuclei (bar = 5 μm). The n represents the total number of examined nuclei. The percentage describes the ratio of the nuclei showing the H3 distribution pattern out of total examined nuclei. DAPI indicates the DAPI staining of the nucleus. c Metagene plots of H3.1swap and H3.3swap ChIP-seq reads over five groups of genes divided based on their expression levels. The black bar in the x-axis represents genes. TSS transcription start sites, TTS transcription terminal sites; −2 K and +2 K represent 2 kb upstream of TSS and 2 kb downstream of TTS, respectively. The y-axis represents the log2 value of H3.1swap and H3.3swap ChIP-seq reads normalized to those of Col-0. d FLAG-tagged wild-type and mutant H3 proteins have similar post-translational modifications. Immunoblotting showing similar H3K9ac, H3K36me2, and H3K4me3 levels from transgenic plants expressing FLAG-tagged H3 variants. FLAG-tagged H3 proteins were first purified with anti-FLAG beads, and then immunoblotted with respective antibodies to determine the histone modification levels. e Boxplot shows the log2 value of ChIP-seq reads of wild-type and mutant H3 normalized to those of Col-0 over the top 100 highly expressed housekeeping genes. f Summary of the genomic distribution patterns of H3.1, H3.3, and their respective mutants. g A working model for Phe41 function in H3.1 distribution. The yeast and green algae contain one single H3 (likely the H3 ancestor) that serves as a substrate for both replication-dependent and replication-independent deposition pathways for nucleosome assembly. In vascular plants, F41 of H3.1 may play an important role in histone deposition and/or histone replacement by restricting H3.1 in the silent and heterochromatic regions. H3.3swap and H3.1F41Y mutation may prevent this restriction resulting in the accumulation of H3.1 in both active and silent genes