Figure 7.
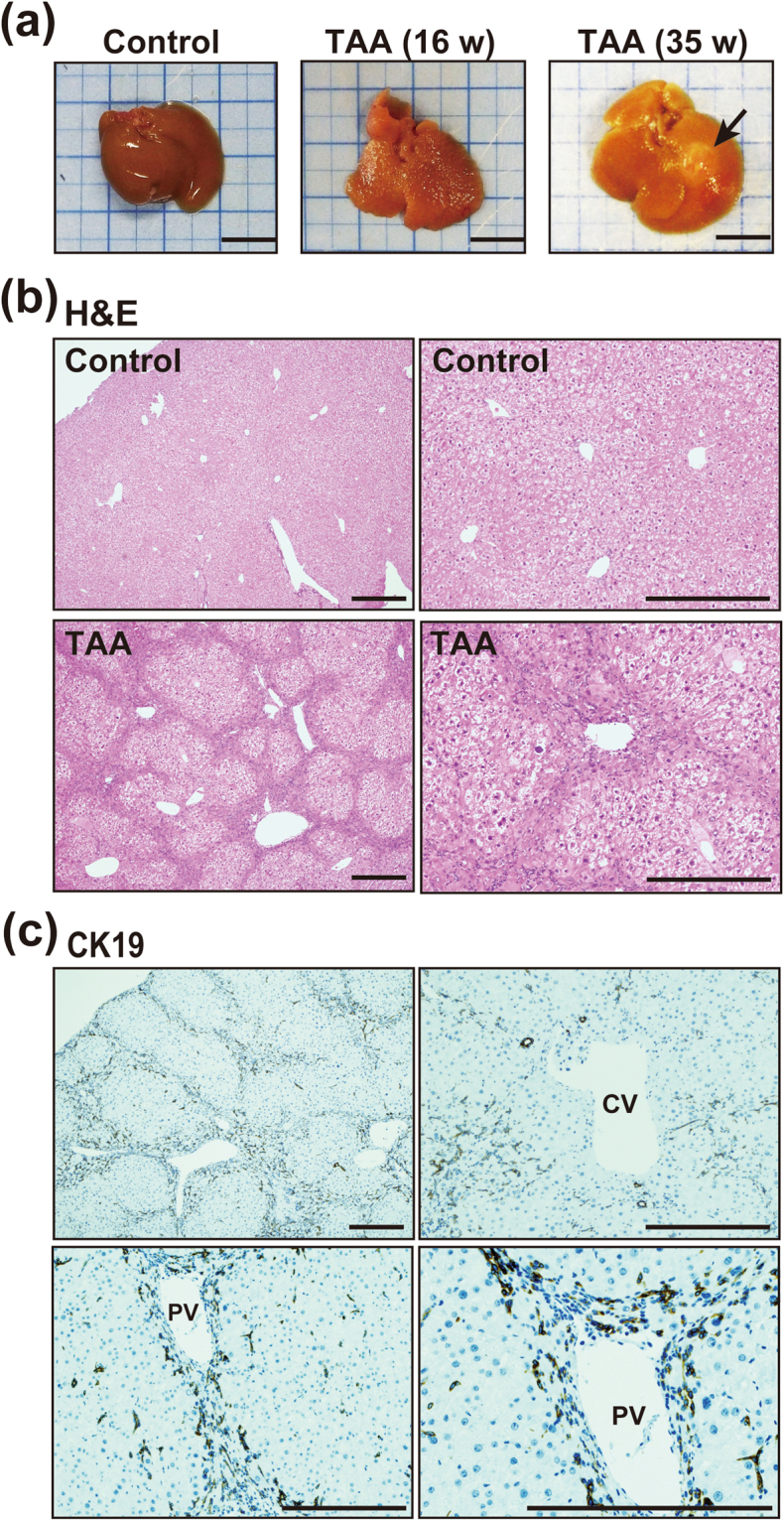
TAA-induced liver injury may promote conversion of hepatocytes to biliary lineage cells. (a) Macroscopic appearance of the liver of mice administered TAA for 16 and 35 weeks. Administration of TAA induced prominent inflammation in the liver by16 weeks and development of liver tumors (arrow) by 35 weeks. Scale bars: 10 mm. (b) H&E staining of the liver of control mice and mice administered TAA for 16 weeks. Administration of TAA induced prominent inflammation and fibrosis around Glisson’s capsule in the liver by 16 weeks and development of liver tumors by 35 weeks. Scale bars: 300 μm. (c) Immunohistochemical staining of CK19 in the liver of control mice and mice administered TAA for 16 weeks. The cholangiocyte marker CK19 was strongly expressed in cells around portal veins (PV) in the liver, whereas cells around central veins (CV) showed no expression of CK19. Scale bars: 300 μm.
