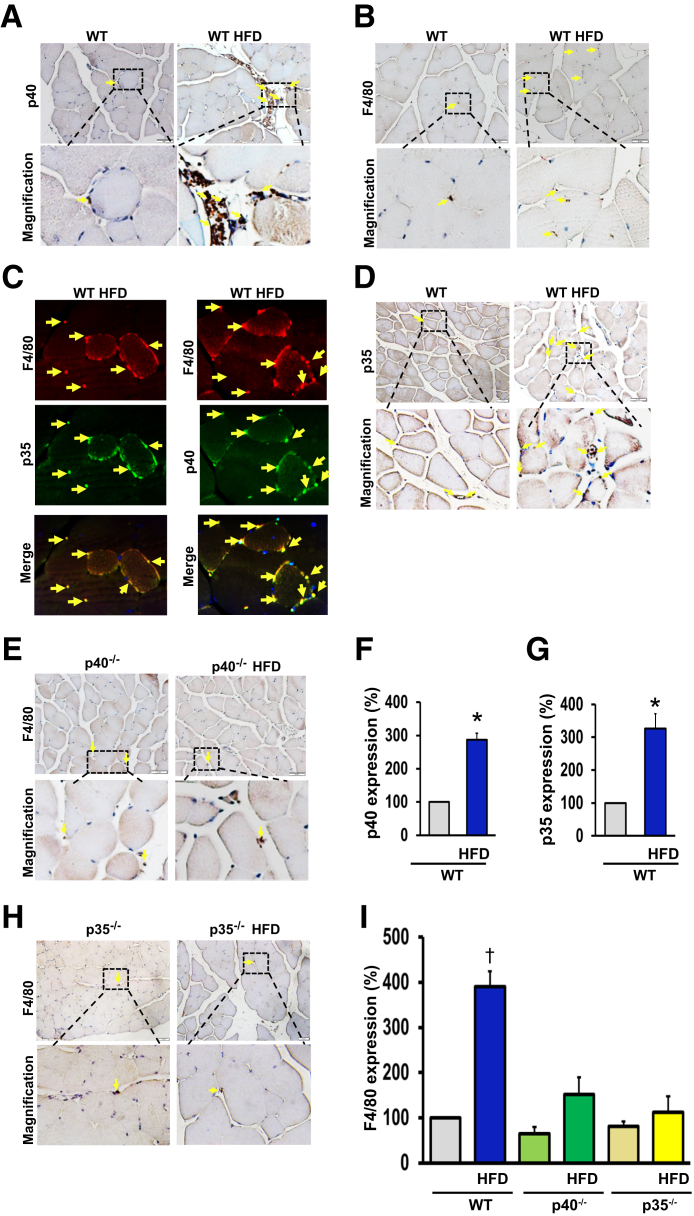
Figure 5.
A and B: Immunohistochemistry images using p40 and p35 antibodies to detect p40 and p35 IL-12 in the hind-limb ischemic muscle of wild-type (WT) mice fed a chow diet or a high-fat diet (HFD). C and D: Quantification of immunohistochemistry staining for p40 and p35 of WT mice fed a chow diet or an HFD. E–G: Immunohistochemistry images using F4/80 antibody to detect macrophages in hind-limb muscle of WT (E), p40−/− (F), and p35−/− (G) mice fed a chow diet or an HFD. H: Quantification of immunohistochemistry images for F4/80 in hind-limb muscle of WT, p40−/−, and p35−/− mice fed a chow diet or an HFD. I: Double immunofluorescence for p40 (green), p35 (green), and the macrophage marker F4/80 (red) using specific antibodies, followed by fluorescent-labeled secondary antibodies, in hind-limb muscle of WT mice fed an HFD. Arrows show the specific staining for each antibody. All of the data shown are representative of six separate animals. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. ∗P < 0.05 versus WT; †P < 0.05 versus all groups. Original magnification, ×20 (A, B, D, E, and H); ×50 (C).