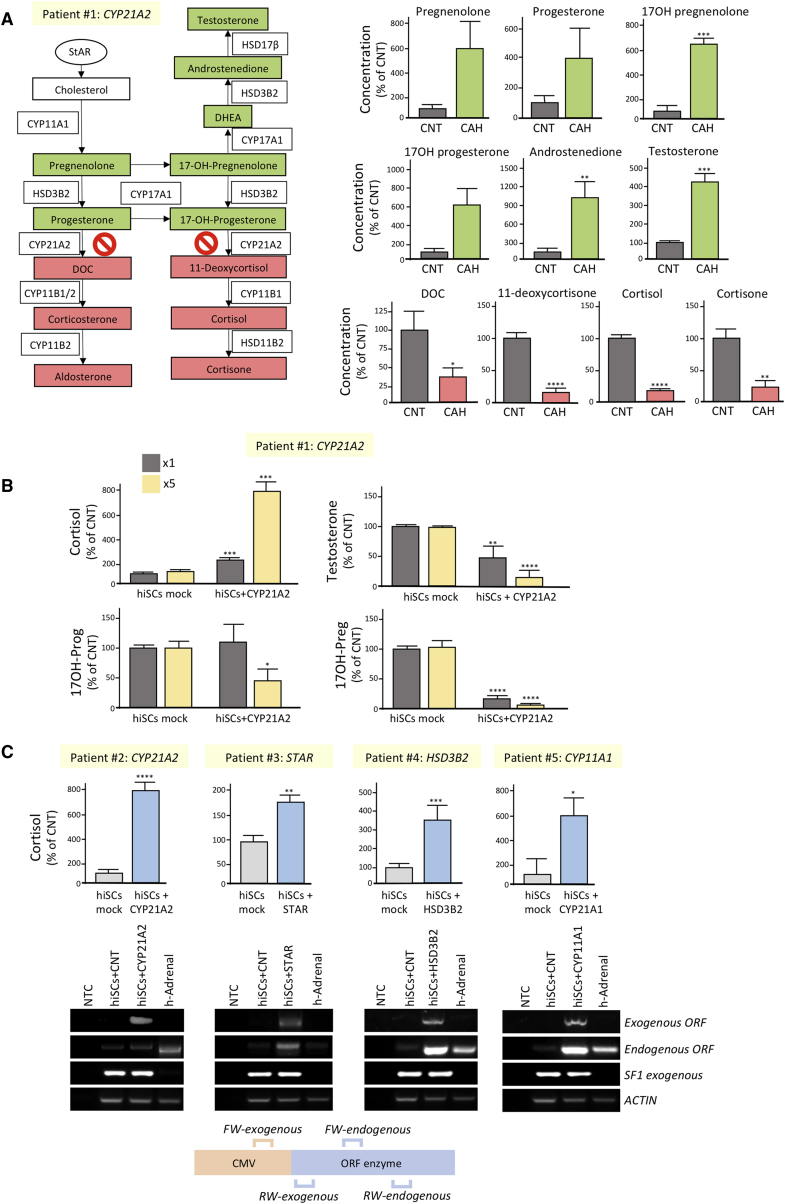
Figure 5.
Characterization of Urine-Derived hiSCs Established from Patients with CAH
(A) Comparison of steroidogenic profile of hiSCs established from patient #1 with CYP21A2 mutation (CAH) versus healthy donors (CNT). The diagram on the left shows the steroidogenic pathway with increased metabolites in patient #1 highlighted in green and decreased ones in red.
(B) Comparison of cortisol, 17-hydroxyprogesterone, 17-hydroxypregnenolone, and testosterone levels of hiSCs derived from patient #1 with or without restoration of the wild-type form 21-OH. Cells were infected with two increasing amounts of lentiviral particles (×1 and ×5).
(C) Comparison of cortisol levels of hiSCs derived from patients (#2–#5) with several forms of CAH with or without restoration of the wild-type form of the corresponding steroidogenic enzymes. RT-PCR analyses using primers encompassing coding- and vector-specific regions confirmed the expression of the exogenous enzymes (lower panels). See also Table 1. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, n ≥ 3.