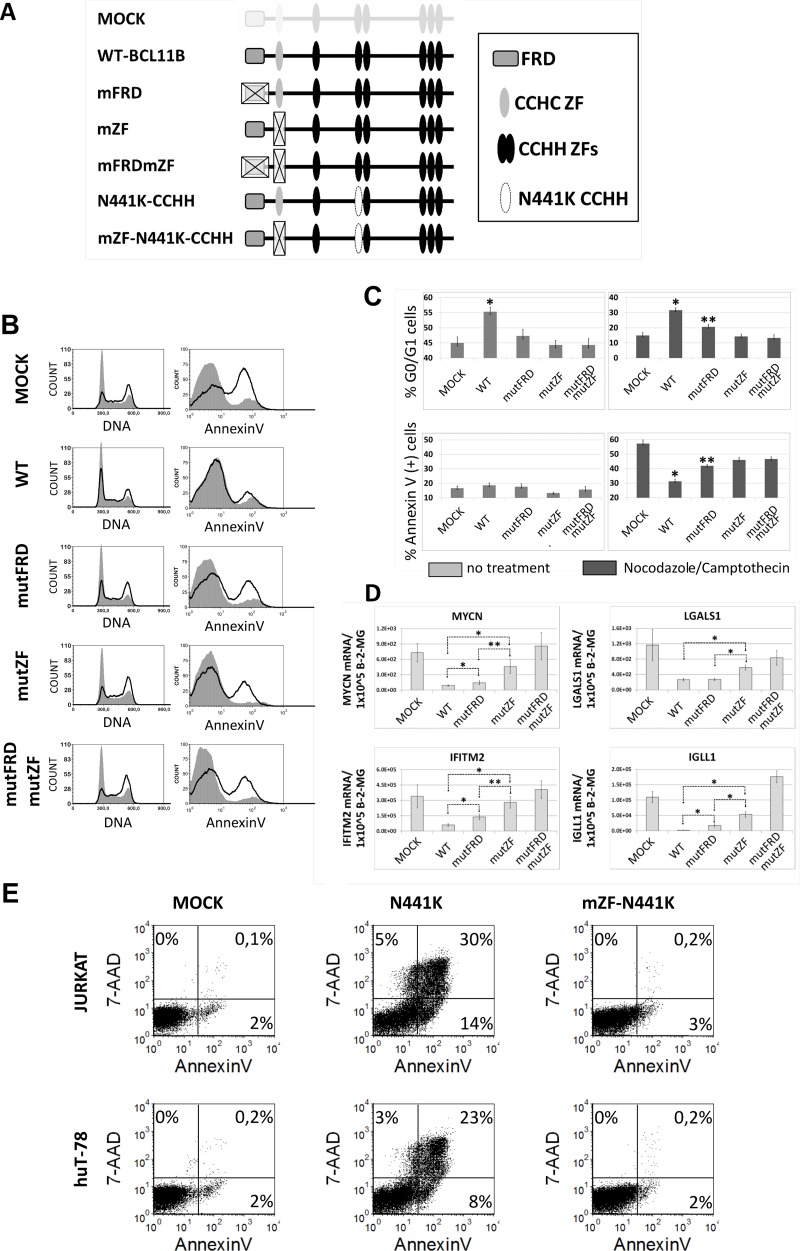
FIG 5.
The CCHC domain of BCL11B is crucial for its influence on cell cycle progression, apoptosis resistance, and transcriptional activity. (A) Schematic drawing of full-length BCL11B variants created to verify the functions of FRD and CCHC domains. (B) Representative cell cycle and apoptosis results obtained with huT-78 cells transduced with wt or mutant BCL11B. Cells were left untreated or incubated with nocodazole, which blocks the cell cycle at G2/M phase (left). Apoptosis was induced with the topoisomerase inhibitor camptothecin (right). (C) Mean percentages of G0/G1 (±SD) and annexin V-positive cells after transduction with different BCL11B variants. The cells were incubated with nocodazole (cell cycle) or camptothecin (apoptosis). (D) Relative levels of mRNAs for genes attenuated after BCL11B overexpression compared to beta-2-microglobulin housekeeping gene (B-2-MG). (E) Jurkat and huT-78 cells were transduced with vectors encoding EGFP (mock), dominant-negative BCL11B (N441K), or N441K with a mutated CCHC motif. Apoptosis was measured 48 h after transduction by annexin V/7-aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD) staining, followed by FACS. All the data were obtained from at least three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.05.