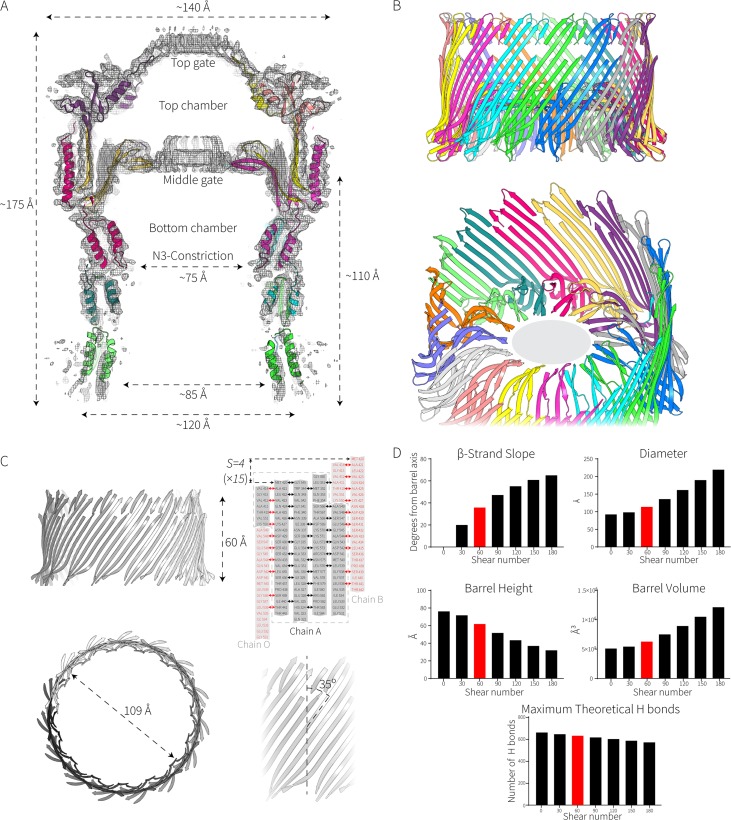
FIG 2.
Elongated β-strands in the EPEC secretin determine its cavity diameter. (A) Slice through the Falcon II map showing the fitted model of the complex. The dimensions of the complex are shown. (B) Zoom views of the double β-barrel. The gray ellipse (in the lower panel) represents the unassigned density in the middle gate corresponding to amino acids 462 to 473. (C) Properties of the giant β-barrel, including calculations of its shear number (S) and diameter. (D) How shear affects the properties of a β-barrel. The values presented here are derived from the formulas tan α = Sα/nb and R = b/[2 sin (π/n)cos α] described in the work of Murzin et al. (72), where α is the average slope of the strands in the barrel, R is the radius of the barrel, a is the Cα-to-Cα distance along the peptide, b is the interstrand distance, n is the number of strands, and S is the shear number. Shear numbers of S = 0 to S = 3n are shown in the graphs. The maximum theoretical H bonds are calculated assuming that every other residue is bonded to the adjacent residue on the next strand.