FIG 7.
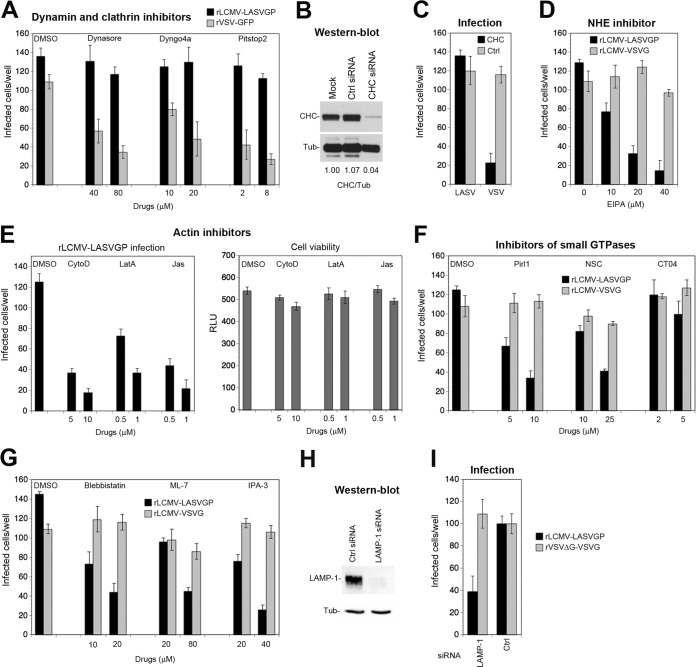
Axl-dependent LASV cell entry involves macropinocytosis and requires LAMP-1. (A) Axl-mediated entry of rLCMV-LASVGP is independent of dynamin and clathrin. HT-1080 cells were pretreated with inhibitors for dynamin-2 (Dynasore, Dyngo 4a) and clathrin (pitstop-2) at the indicated concentrations for 30 min, followed by infection with rLCMV-LASVGP (300 PFU/well) and rVSV-GFP (100 PFU/well) in complete medium in the presence of drugs. After 1 h, cells were washed 3 times with medium containing 20 mM ammonium chloride, followed by incubation in the presence of the agent. After 16 h, the cells were fixed, and infection was detected by IFA using MAb 113 to LCMV NP as described for Fig. 3B. Infection with rVSV-GFP was assessed after 8 h by detection of the enhanced-GFP reporter by direct-fluorescence microscopy. (B) Depletion of the clathrin heavy chain (CHC) by RNAi. HT-1080 cells were either transfected with a pool of siRNAs specific for the clathrin heavy chain or control scrambled siRNAs or mock transfected as described for Fig. 3C. After 72 h, expression of the clathrin heavy chain was detected in a Western blot using α-tubulin (Tub) as a loading control. The efficiency of clathrin heavy-chain depletion was assessed by densitometry, followed by calculation of the signal ratios of the clathrin heavy chain/α-tubulin (CHC/Tub). (C) HT-1080 cells subjected to RNAi were infected with rLCMV-LASVGP (LASV) at 300 PFU/well and rLCMV-VSVG (VSV) at 100 PFU/well for 1 h. Infection was detected by IFA as described for panel A. Data represent means ± SD (n = 3). (D) The amiloride drug EIPA blocks Axl-mediated entry of rLCMV-LASVGP. HT-1080 cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of EIPA for 30 min, followed by infection with rLCMV-LASVGP (300 PFU/well) and rLCMV-VSVG (100 PFU/well) in the presence of drugs for 1 h, and infection was detected by IFA as described for panel A. (E) Actin inhibitors block Axl-dependent rLCMV-LASVGP infection without causing cell toxicity. HT-1080 cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of cytochalasin D (CytoD), latrunculin A (LatA), and jasplakinolide (Jas) for 30 min, followed by infection with rLCMV-LASVGP (300 PFU/well) as described for panel A. Data are means ± SD (n = 3). Cell viability was monitored by the CellTiter-Glo assay as described in Materials and Methods by measuring cellular ATP levels in a luminescence assay. Data are displayed in relative light units (RLU) and are means ± SD (n = 3). (F) Axl-mediated entry of rLCMV-LASVGP depends on Cdc42 and Rac1 but not RhoA. HT-1080 cells were pretreated with a DMSO vehicle control or the inhibitors Pirl1 (Cdc42), NSC23766 (Rac1), and CT04 (RhoA) at the indicated concentrations, followed by infection with rLCMV-LASVGP (300 PFU/well) and rLCMV-VSVG (100 PFU/well) for 1 h in the presence of drugs, and infection was detected as described for panel A. Values are means ± SD (n = 3). (G) Axl-dependent entry of rLCMV-LASVGP requires PAK1, non-muscle myosin II, and myosin light-chain kinase. HT-1080 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of IPA-3, blebbistatin, and ML-7, followed by infection with rLCMV-LASVGP (300 PFU/well) and rLCMV-VSVG (100 PFU/well) as described for panel D. Data are means ± SD (n = 3). (H) Knockdown of LAMP-1 by RNAi. HT-1080 cells were transfected with siRNAs specific for LAMP-1 and control scrambled siRNAs. After 48 h, depletion of LAMP-1 was verified in a Western blot using α-tubulin (Tub) as a loading control. (I) Axl-dependent infection of rLCMV-LASVGP depends on LAMP-1. LAMP-1-depleted and control HT-1080 cells were infected with rLCMV-LASVGP at 300 PFU/well and rVSVΔG-VSVG (100 PFU/well) for 1 h. Infection was detected by IFA as described for panel A. Data are means ± SEM (n = 3 for rLCMV-LASVGP and n = 2 for rVSVΔG-VSVG).