Fig. 2.
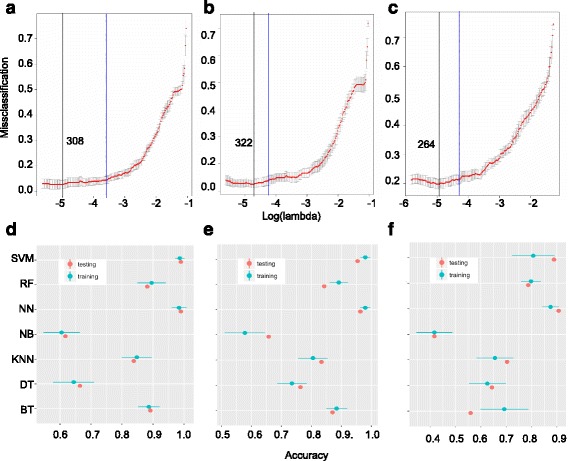
Feature selection and model tuning results. Panels (a), (b), and (c) show the results of applying the LASSO regression process by using both protein-coding genes, protein-coding genes only, and long non-coding RNAs only, respectively. The x-axis is the tuning parameter in log-scale and the y-axis is the 10-fold cross-validated misclassification error. The black vertical line indicates the optimal model with the lowest misclassification error, the blue vertical line indicates a lesser complex model with misclassification error within one standard error of the optimal model. The number indicated next to the black vertical line is the number of predictors selected by the optimal LASSO regression model. Panels (d), (e), and f show the prediction accuracy results of 7 predictive models (SVM: support vector machines, RF: random forest, NN: neural network, NB: Naïve Bayes, KNN: k-nearest neighbor, DT: decision trees, BT: boosted trees) using the reduced set of predictors from panel (a), (b), and (c), respectively. The prediction accuracies for training and testing sets are indicated
