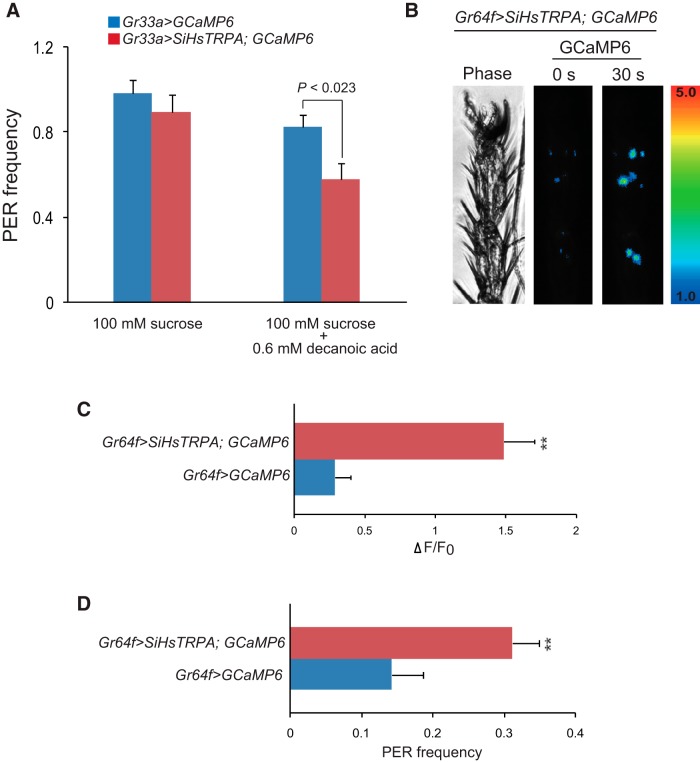
Figure 9.
Decanoic acid modifies gustatory responses of D. melanogaster expressing SiHsTRPA. A, PER frequency of fruit flies expressing either GCaMP6 (Gr33a > GCaMP6) alone or both GCaMP6 and SiHsTRPA (Gr33a > SiHsTRPA; GCaMP6) under Gr33a-Gal4 toward 100 mm sucrose solution containing 0 (n = 19–20 for each genotype) or 0.6 mm decanoic acid (n = 19–21 for each genotype). The mean value with error bar (± SEM) is shown. PER frequency of fruit flies expressing both GCaMP6 and SiHsTRPA is significantly lower than that of those expressing GCaMP6 alone toward 100 mm sucrose containing 0.6 mm decanoic acid (two-tailed t test). B, Phase and GCaMP6 images of fruit fly expressing both SiHsTRPA and GCaMP6 under Gr64f-Gal4 (Gr64f > SiHsTRPA; GCaMP6) before (0 s) and 30 s after applying 0.6 mm decanoic acid to the distal segments of the foreleg. The increase of GCaMP6 fluorescence (ΔF) is indicated by pseudo-color. A, Intracellular calcium changes (ΔF/F0) of SiHsTRPA and GCaMP6- or GCaMP6-expressing sugar taste neuron associated with 5D1 sensilla 30 s after applying 0.6 mm decanoic acid (n = 6–9). **, Intracellular calcium level is significantly higher, with fruit flies expressing both SiHsTRPA and GCaMP6 than those expressing GCaMP6 alone (two-tailed t test, P < 0.0009). D, PER frequency of fruit flies of Gr64f > SiHsTRPA; GCaMP6 and Gr64f > GCaMP6 stimulated by 0.6 mm decanoic acid (n = 29). **, Fruit flies expressing both GCaMP6 and SiHsTRPA show significantly higher PER frequency than those expressing GCaMP6 alone (two-tailed t test, P < 0.0049).