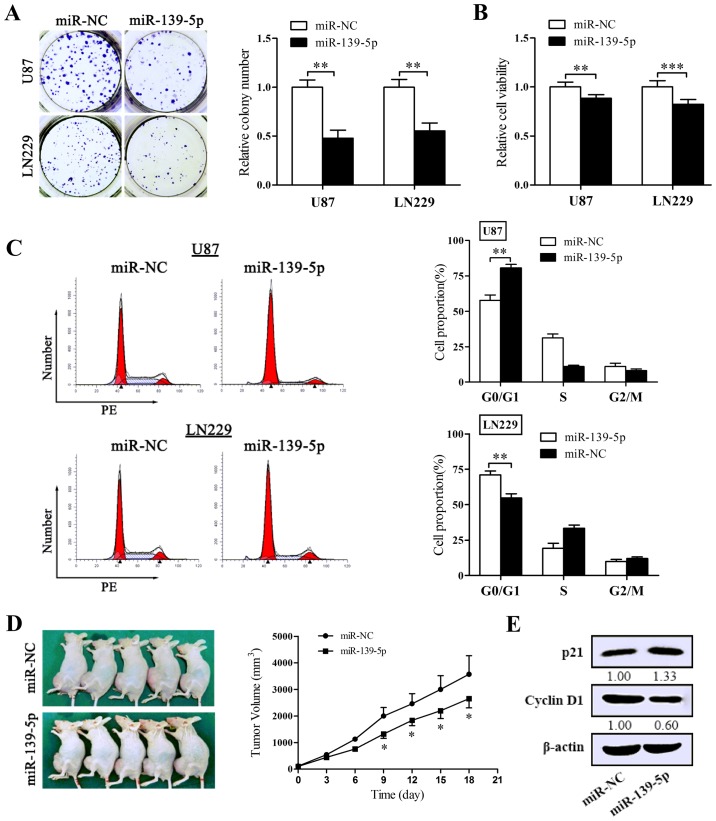
Figure 3.
Restoration of miR-139-5p expression inhibits tumor proliferation in vitro and in vivo and blocks the cell cycle progression. (A) Colony formation assay was performed to examine the impact of miR-139-5p on proliferation of U87 and LN229 cells. Cells were cultivated for 14 days before being fixed and stained. (B) Cellular viability assay. The cell viability of transfected U87 and LN229 cells was determined via MTT assay 72 h after transfection. (C) The cell cycle progression of U87 and LN229 cells was determined by flow cytometry. The DNA content was measured via propidium iodide (PI) staining. The charts (right) show the population of cells in G0/G1, S and G2/M phase. (D) Xenograft nude mouse model (n=5) was obtained, following which miR-139-5p mimics or miR-NC were intratumorally delivered every 3 days. Tumor volumes following miR-139-5p administration were significantly reduced. Photography of the xenograft tumor-bearing mice and the tumor growth curve are shown. (E) The influence of miR-139-5p on the protein levels of proliferation-associated molecules (p21, cyclin D1) were determined by western blotting. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001.