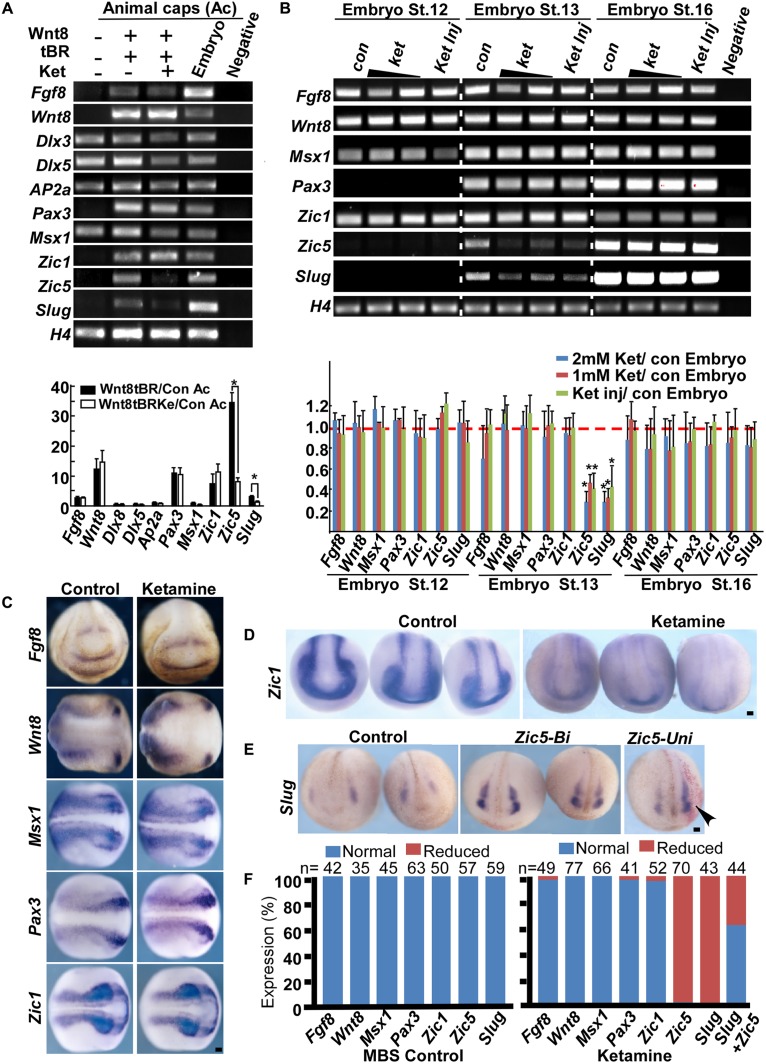
FIGURE 3.
Ketamine targets Zic5 in NC induction. (A) In animal caps, Wnt8 (500 pg) and tBR (500 pg) induce expression of NC markers (lanes 1, 2). Upon ketamine exposure, the expression of Zic5 and Slug were inhibited (lanes 2, 3). The induced expression of Zic5 and Slug were reduced by ketamine treatment in animal cap. Gene expressions were normalized with H4. Data are shown as folds over the control animal caps. 15 animal caps were isolated for each group for single time experiments. The number represents Mean ± SEM, N = 3, ∗P < 0.05 by ANOVA. (B) In whole embryos, either ketamine exposure or injection (0.8 nmol/embryo) blocked Zic5 and Slug expression at stage 13 (when the NC is being induced) but not stage16 (at the onset of NC migration). Ketamine treatment did not affect most of the border genes from stage 12 to stage 16, but significantly blocked Zic5 and NC gene Slug at stage 13. For a single time experiment, 10 embryos were collected for each group for RT-PCR. Data are shown as folds over the control embryos. The number represents Mean ± SEM. N = 3, ∗P < 0.05 by ANOVA. (C) In situ hybridization suggests genes involved in NC induction, including Fgf8, Wnt8, Msx1, Pax3, and Zic1 were not affected by ketamine exposure. (D) Ketamine inhibited Zic5 expression comparing with MBS cultured control group. (E) The inhibition of Slug expression by ketamine was rescued by injection of Zic5 mRNA (500 pg) in both sides or unilaterally. Arrowhead indicate the unilaterally injected side. (F) Quantitative analysis of in situ hybridization results, left: MBS control group, right: ketamine exposure group. ∗P < 0.05 with t-test. Con, control; Ket, ketamine; Ket Inj, ketamine injection; St., stage; Zic5-Bi, zic5 bilateral injection; Zic5-Uni, zic5 unilateral injection. Scale bar: 100 μm.