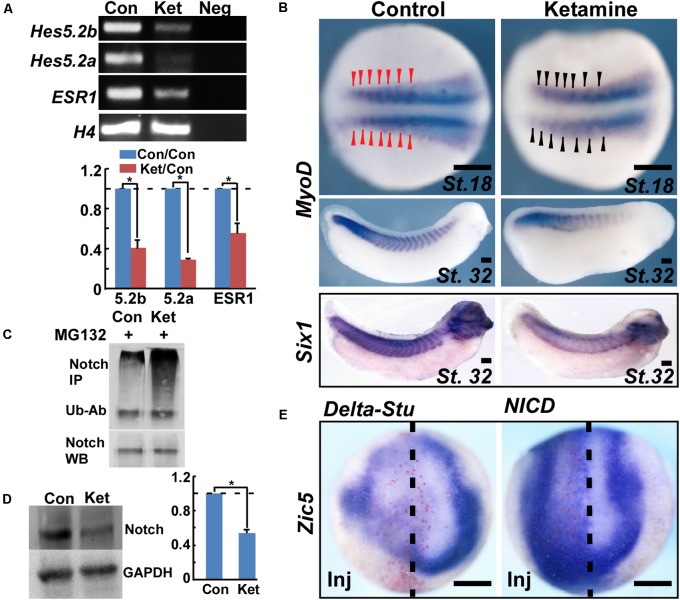
FIGURE 4.
Ketamine inhibits Zic5 through the Notch signaling pathway. (A) During NC induction, ketamine exposure down-regulated expression of Notch targeted genes including Hes5.2a, Hes5.2b, and ESR1. The number represents Mean ± SEM, N = 3, ∗P < 0.05 by Student’s t-test. (B) In the late neurula, MyoD transcription in early somite primordium became a little bit thin and slightly reduced the signal upon ketamine exposure. At tailbud stage, ketamine led to fewer somites and a shortened body axis. The somites are labeled with in situ hybridization of MyoD, and Six1. (C) Ketamine exposure increased the amount of ubiquitinated Notch protein in Jurkat cells. Upper part: ubiquitinated Notch proteins were immuno-precipitated (IP) with Notch-1 antibody, followed by anti-ubiquitin antibody (Ub-Ab) western blot staining. Lower part: Notch-1 loading control. (D) In Jurkat cells, ketamine exposure for 10 h reduced Notch protein level. The number represents Mean SEM, N = 3, P < 0.05 by Student’s t-test. (E) During NC induction, inhibiting Notch signaling by microinjection of 1 ng Delta-stu mRNA at 4-cell stage blocked Zic5 expression. Activation of Notch signaling by microinjection of 800 pg NICD mRNA into one dorsal cell at 4-cell stage induced ectopic Zic5 expression. Scale bar: 100 μm.