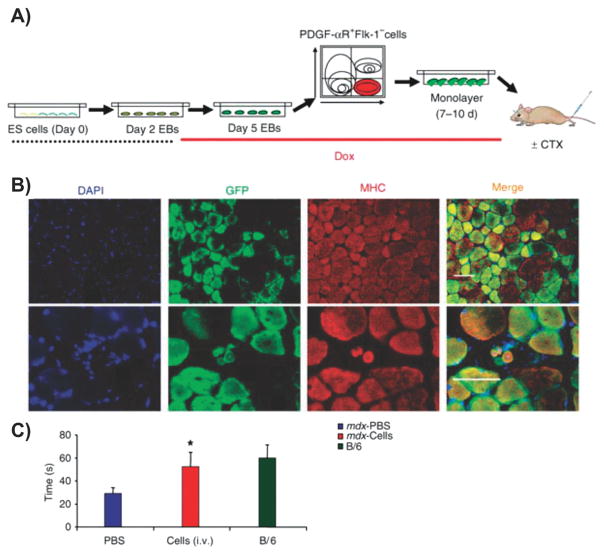
Figure 16.
Engineering embryonic stem cells with Pax3 to induce differentiation to skeletal muscle for the treatment of muscular dystrophy. A) Doxycyline-induced cell monolayers resulting from PDGF-αR+Flk-1− sorted cells from day 5 embryoid bodies were transplanted by various routes of administration (i.m., i.v. and i.a.) into Rag2−/−γc−/− immunodeficient mice or mdx mice (with or without cardiotoxin (CTX) pre-injury). B) Analyses of Rag2−/−γc−/− mice (pre-injured with cardiotoxin) 30 d after i.m. transplantation (n = 8 mice). Shown is immunostaining for GFP (green) and MHC (red). Top and bottom rows show different magnifications. Scale bars, 100 μm. C) Performance on the rotarod was assessed in mdx mice pre-injured with cardiotoxin (both legs) and treated with PBS (control, blue) or i.v. cell transplantation (red). B/6 mice (green) also pre-injured with cardiotoxin (both legs) were analyzed as a reference. *p < 0.05. Reproduced with permission.[298] Copyright 2008, Nature.