Figure 5.
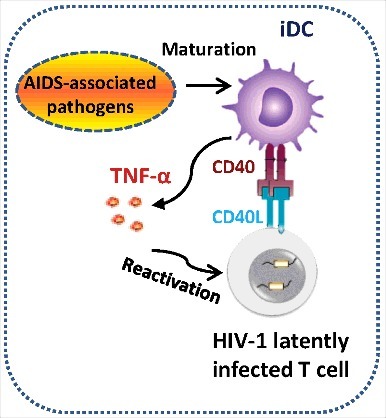
Schematics illustrating the role of DCs in triggering HIV-1 reactivation. AIDS-associated pathogens (such as M. bovis BCG) or bacterial compound LPS mature DCs to secrete TNF-α into the supernatant to reactivate HIV-1 from latency. Alternatively, co-culture with HIV-1 latently infected T cells mature DCs through CD40-CD40L signaling pathway, and these matured DCs secrete TNF-α to activate T cells, allowing HIV-1 reactivation.
