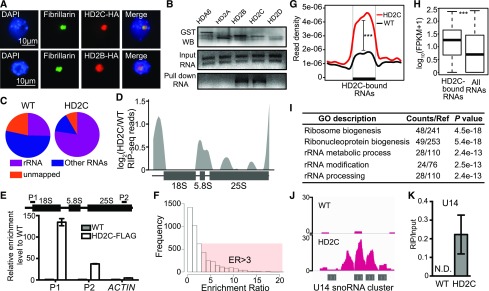
Figure 8.
HD2C Is Associated with Pre-rRNAs and SnoRNAs.
(A) Immunostaining for protein localization of HD2C and HD2B. Fibrillarin was used as a nucleolar marker.
(B) In vitro RNA pull-down assay of HD2C and HD2B. Bands in “GST WB” indicate immunoblots of GST-tagged protein. Bands in “Input RNA” and “Pull down RNA” indicate ethidium bromide staining of rRNA.
(C) Distribution of RIP-seq reads of HD2C and the wild type. rRNA represents the reads mapped to rRNA sequence, and non-rRNA represents reads mapped to other RNAs except rRNA.
(D) HD2C binding peaks on rRNA precursor. y axis represents the log2 value of HD2C RIP-seq normalized with the wild type.
(E) RIP-qPCR confirmation of HD2C binding on rRNA. ACTIN served as a control.
(F) Histogram of frequency distribution of HD2C enrichment ratio on RNAs. ER, enrichment ratio.
(G) Metaplots of HD2C enrichment on HD2C-bound RNAs. y axis represents the read density of RIP-seq. Student’s t test, ***P < 0.001.
(H) Box plots show the abundance of HD2C-bound RNAs and average of all RNAs. y axis represents the log10 value of FPKM+1. Student’s t test, ***P < 0.001.
(I) GO analysis of HD2C-bound RNAs.
(J) Snapshot of HD2C binding peaks on U14 snoRNA cluster RNA transcript.
(K) RIP-qPCR validation of HD2C binding on U14 snoRNA. N.D., not detected.