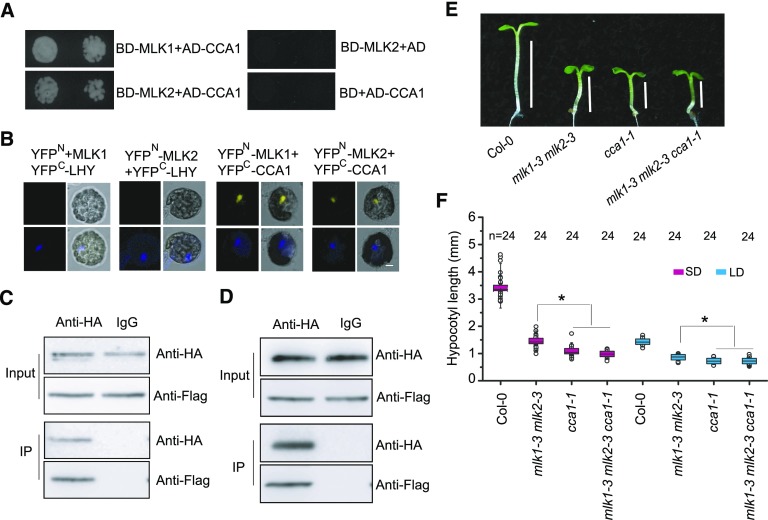
Figure 4.
MLK1 and MLK2 Interact with CCA1.
(A) Yeast two-hybrid analysis revealing an interaction between MLK1/2 and CCA1. The growth of two concentrations (2 × 10−2 and 2 × 10−3) of yeast cultured on synthetic defined medium lacking Trp, Leu, His, and adenine is shown.
(B) MLK1/2 fused to the N terminus of YFP (YFPN) or the N terminus of YFP alone were tested for their ability to bind to the C terminus of YFP (YFPC) fused to LHY or the C terminus of YFP fused to CCA1. Yellow fluorescence and a bright-field image were recorded and the resulting images were merged. Twenty-five cells were examined for each transformation. Bar = 10 µm.
(C) and (D) Co-IP between MLK1/2 and CCA1. FLAG-MLK1/2 and HA-CCA1 were cotransformed into Arabidopsis protoplasts, immunoprecipitated using an anti-HA antibody, and detected with anti-Flag and anti-HA antibodies. The cells were harvested at 2 h after lights-on zeitgeber time (ZT2).
(E) Representative image of Col-0, cca1-1, mlk1-3 mlk2-3, and cca1-1 mlk1-3 mlk2-3 under SD. Lines indicate hypocotyl lengths.
(F) The hypocotyl lengths of Col-0, cca1, mlk1 mlk2, and cca1 mlk1 mlk2 under SD and LD. Means ± sd obtained from independent plants. Asterisks indicate significant difference using Student’s t test (P < 0.05).