Figure 9. Immunohistochemistry of infiltration of CD4+ T cells into the valve of the left atrium in ARF.
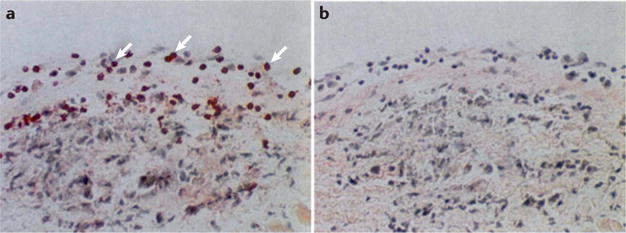
In acute rheumatic fever (ARF), CD4+ T cells cross the valvular endothelium and infiltrate into the subendocardium, where they are involved in the formation of Aschoff’s bodies. a | An Aschoff body, with CD4+ T cells in the valve (red, indicated with arrows) labelled with a primary monoclonal antibody against CD4, secondary antibody against human IgG and fast red. b | An IgG1 isotype control did not react with the rheumatic valve. CD4+ T cells are stained with the CD4-specific mAb, a secondary antibody conjugated to alkaline phosphatase and development with fast red to detect antibody binding to CD4+ T cells. Magnification 200×. Image is modified, with permission, from REF. 87 © (2001) American Society for Microbiology.
