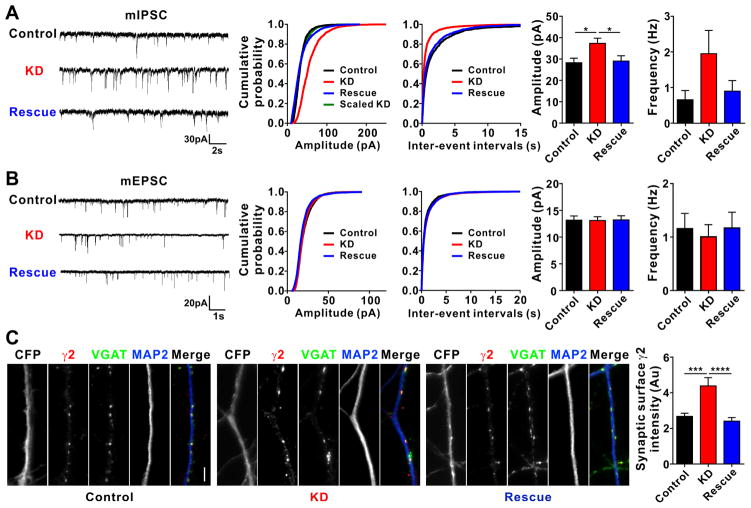
Figure 5. Knockdown of Clptm1 Scales Up Inhibitory Synaptic Strength.
Cultured hippocampal neurons were transfected with U6-shScramble-hSyn-CFP and hSyn-YFP as control, U6-shClptm1-hSyn-CFP and hSyn-YFP as knockdown (KD), or U6-shClptm1-hSyn-CFP and hSyn-YFP-p2a-Clptm1* as rescue at 0 DIV. CFP and YFP dual positive neurons were selected for recording or immunostaining. mIPSCs were recorded at 13 DIV, mEPSCs were recorded at 14 DIV, and immunostaining was performed at 14 DIV.
(A) Knockdown of Clptm1 significantly increased mIPSC amplitude compared with the control group, an effect rescued by expressing the shRNA-resistant Clptm1*. n=17–19 cells from 4 independent experiments, p<0.05 one-way ANOVA and * p<0.05 post hoc Holm-Sidak tests. The cumulative probability curve of KD amplitude was scaled by dividing by a factor of 1.65. KS test showed no significant difference between control and scaled KD groups.
(B) Knockdown of Clptm1 did not affect mEPSC amplitude or frequency. n=16–18 cells from 4 independent experiments.
(C) Neurons were immunostained live using anti-GABAAR γ2 antibody, followed by fixation and immunostaining for VGAT and MAP2. Knockdown of Clptm1 significantly increased synaptic surface γ2 intensity, an effect normalized by expressing the shRNA-resistant Clptm1*. Scale bar represents 10 μm. n=30 cells from 3 independent experiments, p<0.0001 one-way ANOVA and *** p<0.001, **** p<0.0001 post hoc Holm-Sidak tests.
Results are expressed as mean ± SEM.