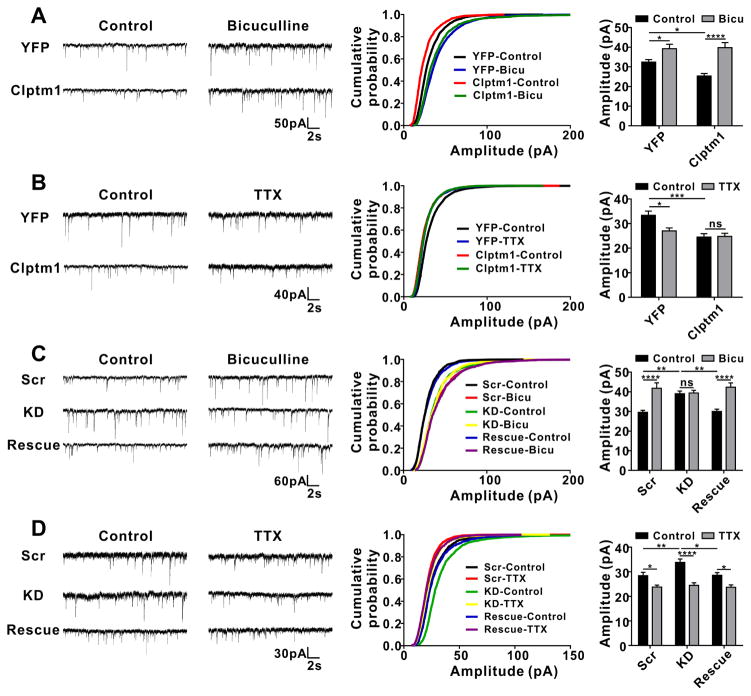
Figure 7. Changes in Expression Level of Clptm1 Occlude Forms of Inhibitory Synaptic Homeostasis.
Cultured hippocampal neurons were transfected at 0 DIV using nucleofection. Bicuculline (Bicu, 10 μM) or TTX (1 μM) was added into culture medium at 14 DIV. mIPSC recordings were performed 24 hours after bicuculline or 48 hours after TTX application.
(A and B) mIPSC amplitude was significantly increased following bicuculline treatment, and decreased following TTX treatment in neurons expressing YFP. Overexpression of YFP-p2a-Clptm1 (Clptm1), which significantly reduced mIPSC amplitude compared with control group YFP, did not affect bicuculline-induced inhibitory synaptic scaling up (A, n=16–17 cells from 2 independent experiments), but blocked TTX-induced scaling down (B, n=19–24 cells from 4 independent experiments). (A) Interaction: p=0.057, expression level of Clptm1: p=0.095, treatment: p<0.0001, two-way ANOVA and * p<0.05, **** p<0.0001 post hoc Holm-Sidak tests. (B) Interaction: p<0.05, expression level of Clptm1: p<0.001, treatment: p<0.05, two-way ANOVA and * p<0.05, *** p<0.001 post hoc Holm-Sidak tests. There was no significant difference between YFP plus bicuculline and Clptm1 plus bicuculline groups, or between YFP plus TTX and Clptm1 plus TTX groups.
(C and D) The transfection groups were U6-shScramble-hSyn-Tdtomato and hSyn-YFP as control, U6-shClptm1-hSyn-Tdtomato and hSyn-YFP as knockdown (KD), or U6-shClptm1-hSyn-Tdtomato and hSyn-YFP-p2a-Clptm1* as rescue. Tdtomato and YFP dual positive neurons were selected for recording. Knockdown of Clptm1, which significantly elevated mIPSC amplitude compared with the control group, did not affect TTX-induced inhibitory synaptic scaling down (D, n=24–30 cells from 5 independent experiments), but blocked bicuculline-induced scaling up (C, n=19–22 cells from 3 independent experiments). The knockdown effects were fully rescued by expressing the shRNA-resistant Clptm1*. (C) Interaction: p<0.001, expression level of Clptm1: p=0.101, treatment: p<0.0001, two-way ANOVA and ** p<0.01, **** p<0.0001 post hoc Holm-Sidak tests. (D) Interaction: p=0.066, expression level of Clptm1: p<0.01, treatment: p<0.0001, two-way ANOVA and * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, **** p<0.0001 post hoc Holm-Sidak tests.
Results are expressed as mean ± SEM
See also Figure S5, S6 and Table S2.