Fig. 4. The rDNA locus and chr XII become increasingly unstable with age.
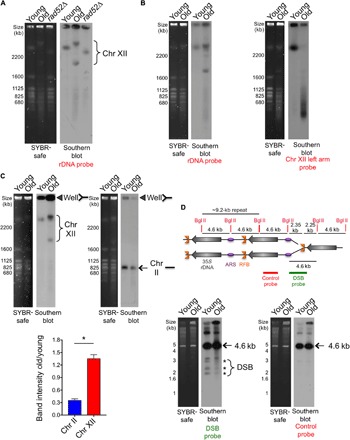
(A) Analysis of yeast chromosomes by PFGE. Left panel: SYBR-safe staining. Right panel: Southern hybridization using a chr XII (rDNA) probe. The rad52Δ mutant was used as a control with a different rDNA copy number. (B) As in (A), probes to the rDNA or the left arm of chr XII on the same samples. (C) Left panel: SYBR-safe staining of same number of cells analyzed by PFGE. Right panel: Southern blot using the indicated probe. Closed triangles indicate stuck DNA in the well. Quantification of the relative intensity of stuck DNA in old cells compared to young cells is shown below with the average and SEM of three replicates. *P < 0.05, significant change, as determined by Student’s t test. (D) The DSB at the RFB is not more abundant in old cells. Schematic showing use of Bgl II digestion to detect DSB at RFB. Southern detection using either the DSB probe or the control probe is shown. The asterisk indicates DNA fragments generated from DSBs near the RFB, whereas the arrows indicate fragments from restriction digestion with no DSB at RFB.
