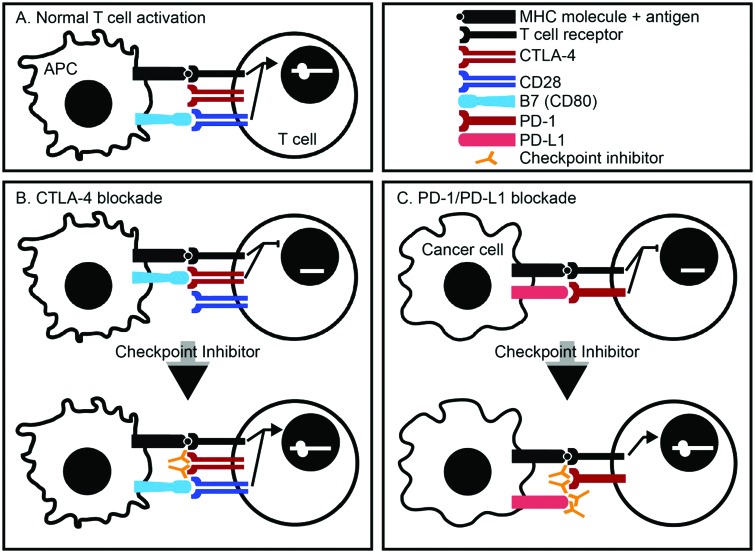
Figure 1.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors.
A. Normal T-cell activation requires two functional synapses: binding of an antigen-containing MHC molecule with a T-cell receptor and binding of the co-stimulatory molecule CD28 found on T cells with B7, found on antigen-presenting cells. B. CTLA-4 is a co-inhibitory molecule present on normal T cells. Binding of CTLA-4 with B7 inhibits activation of T cells. Blocking antibodies against CTLA-4 prevents its binding with B7, thereby allowing for CD28 interaction with B7 and T-cell activation. C. PD-1 is a co-inhibitory molecule present on normal T cells. Its ligand, PD-L1, is upregulated in cancer cells. Blocking antibodies against either PD-1 or PD-L1 allow for T-cell activation.