Figure 5.
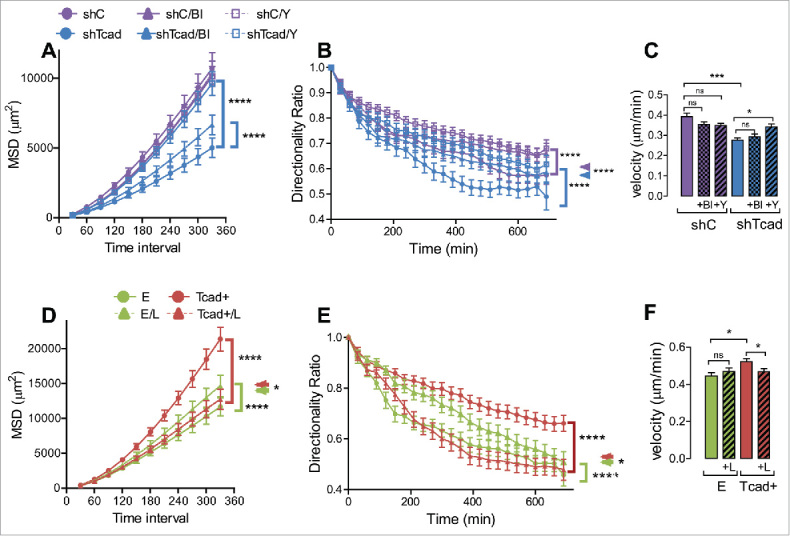
Pharmacological modulation of mechanical actin cytoskeleton properties affects the parameters of random migration. Migration experiments were performed without (control) or with inclusion of polymerized actin content-reducing compound Y-27632 (Y: 5 µM) or actomyosin activity inhibiting blebbistatin (Bl: 1 µM). In the case of shTcad-SMCs (purple) and shC-SMCs (blue) transductants (A-C), or actin polymerization-promoting compound LPA (L: 5 nM) in the case of Tcad+-SMCs (red) and E-SMCs (green) (D-F). Statistical analysis of MSD (A, D) and directionality ratio (B, E) was performed using nonlinear regression analysis. (A) Asterisked brackets indicate significant effects (P < 0.0001) of Bl or Y on the MSD of shTcad-SMCs compared with their untreated counterpart. (B) Asterisked brackets indicate significant effects (P < 0.0001) of either Bl or Y on shC-SMCs (purple bracket) and shTcad-SMCs (blue bracket) as compared with their own corresponding (untreated) control. Asterisked double arrowhead denotes significant differences (P < 0.0001) between shC-SMCs and shTcad-SMCs under each condition (untreated, + Bl or +Y). (D, E) Asterisked brackets indicate significant effects (P < 0.0001) of LPA on E-SMCs (green bracket) and Tcad+-SMCs (red bracket) as compared with their own corresponding (untreated) controls. Asterisked double arrowhead denotes significant a difference (*P < 0.05) between E-SMCs and Tcad+-SMCs in the presence of LPA. (C, F) One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc testing was used for statistical analysis of velocity (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ns, not significant).
