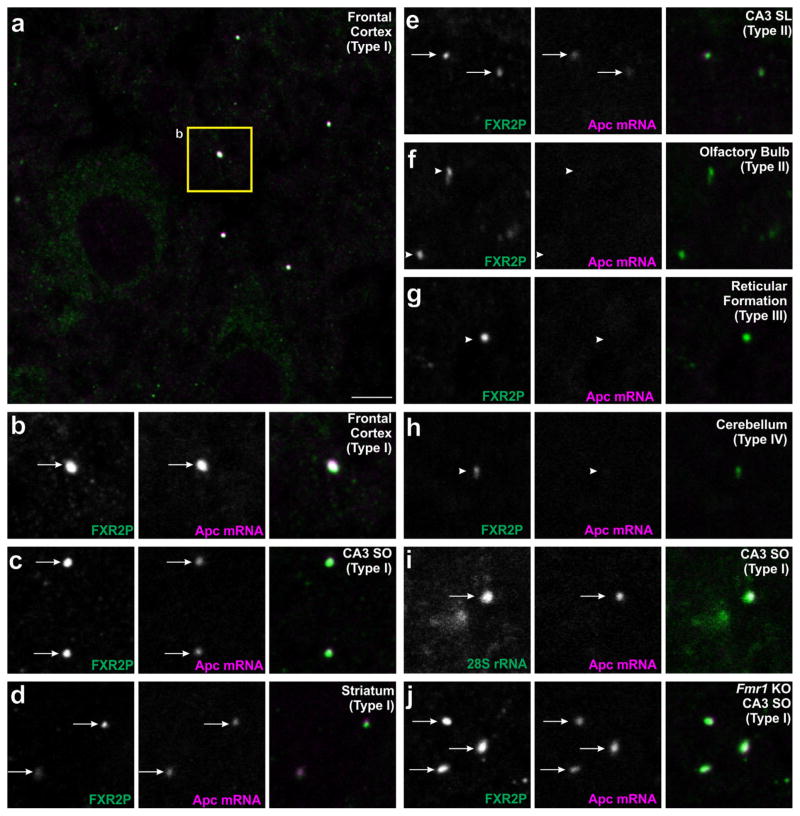
FIGURE 5.
APC mRNA associates with a region-dependent subset of FXGs. Brain sections were double-labeled by in situ hybridization for Apc (red) along with either immunostaining for FXR2P (green; A–H,J) or in situ hybridization for 28S rRNA (green; I). Apc-containing FXGs were observed in a region-dependent subset of Type I FXGs including those in (a–b) axons in frontal cortex, (c) associational fibers in CA3 stratum oriens, and (d) thalamocortical axons in striatum. Apc mRNA also associated with Type II FXGs in (e) hippocampal mossy fibers but not Type II FXGs in (f) olfactory sensory neuron axons in the olfactory bulb. Apc mRNA was not observed in Type III or Type IV FXGs including those in (g) axons in the reticular formation in the medulla or (h) axons in the deep cerebellar molecular layer. (i) Double in situ hybridization for Apc and 28S rRNA showed that Apc-associated FXGs colocalize with ribosomes in CA3 associational fibers. (j) FXGs associate with Apc in CA3 associational fibers in an Fmr1 null mouse. Arrows indicate FXGs that colocalize with Apc. Arrowheads indicate FXGs that do not colocalize with Apc. Scale bar = 10 μm in A, 5 μm in B–L