Figure 3. Applications of fNIRS to various neuroscience studies.
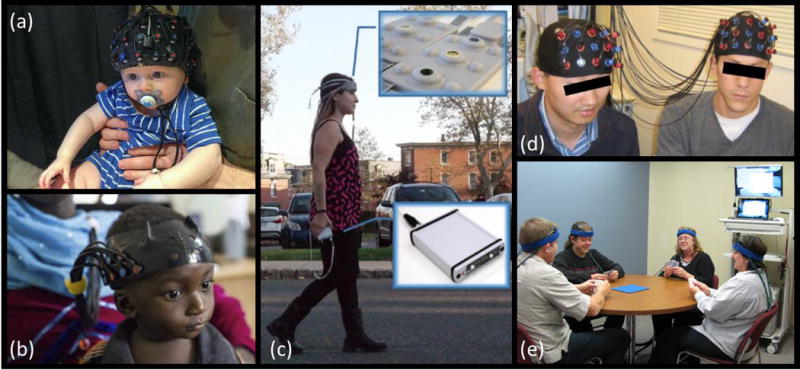
(a) Example of fNIRS cap on the head of a 7-month old infant sitting on his parent’s lap. Photograph courtesy of Dr. Katherine Perdue, Boston Children’s Hospital. (b) fNIRS headgear on a 13-month-old infant. Modified with permission from [42], photo credit to the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. (c) Battery operated and wireless unit allows untethered outdoor measurement during mobility studies. Modified with permission from [49]. (d) Hyperscanning fNIRS experiment simultaneously measuring brain activity in two people while they play a computer-based cooperation game side by side. Modified with permission from [59]. (e) An example of experimental setup for fNIRS hyperscanning of 4 volunteers playing a card game. Photograph courtesy of Arthur DiMartino, TechEn, Inc.
