Table 1. Optimization of the reaction conditions.
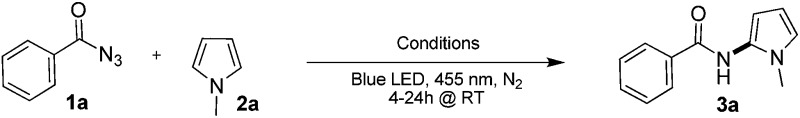
| |||||
| |||||
| Entry | Cat a | Additive b | Solvent | Conv. [%] | Yield c |
| 1 | A | — | DMSO (0.34 M) | ∼35% | — d |
| 2 | A | (BnO)2P(O)OH | DMSO (0.34 M) | 100 | 10 a % |
| 3 | A | (BnO)2P(O)OH | DMSO (0.34 M) | 100 | 30% |
| 4 | A | Benzoic acid | DMSO (0.34 M) | 100 | 8% |
| 5 | A | Acetic acid | DMSO (0.34 M) | 100 | 10% |
| 6 | A | PTSA | DMSO (0.34 M) | 100 | 0% |
| 7 | A | H3PO4 | DMSO (0.34 M) | 100 | 40% |
| 8 | B | H3PO4 | DMSO (0.34 M) | 60 | — |
| 9 | C | H3PO4 | DMSO (0.34 M) | 75 | — |
| 10 | A | H3PO4 | DMF (0.34 M) | 60 | — |
| 11 | A | H3PO4 | ACN (0.34 M) | 20 | — |
| 12 | A | H3PO4 | DMSO (0.09 M) | 100 | 65 e % |
| 13 | A | H3PO4 | DMSO (0.09 M) | 100 | 51 f % |
| 14 | A | H3PO4 | DMSO (0.09 M) | 95 | 30 g % |
| 15 | — | H3PO4 | DMSO (0.09 M) | 0 | — |
| 16 | A | H3PO4 | DMSO (0.09 M) | 0 | — h |
a2.5 mol% of catalyst.
b2 equiv. of additive with respect to 1a.
cIsolated yields.
dPhenylisocyanate and benzamide are obtained.
eReaction conditions: 1a (0.34 mmol, 1 equiv.), 2a (1.7 mmol, 5 equiv.), additives (0.68 mmol, 2 equiv.) and photocatalyst (8.5 μmol, 2.5 mol%) in dry solvent (0.09 M) under N2 was irradiated with blue light for 4 h.
f1 mol% of the catalyst used.
g1 equiv. of N-methylpyrrole.
hWithout light.
