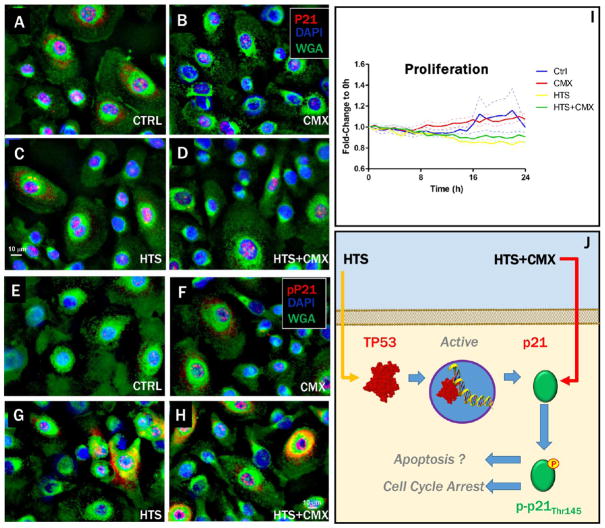
Figure 3.
Dependency of cytosolic and nuclear localization of p21 on T145 phosphorylation and correlation with HTS inhibitory effect on proliferation. Expression of p21 in SAECs was enhanced by the HTS treatment (A–D). HTS treatment, alone or in combination with CMX, promoted phosphorylation of p21 on T145, which prevented nuclear translocation and promoted cytosolic localization (E–H). Increased p21 expression and phosphorylation after treatment with HTS inhibited cell proliferation over 24 h (I). Inhibition of proliferation mediated by HTS effect on p21 may result in either cell-cycle arrest or apoptosis, depending on cytosolic vs nuclear localization of p21, which is in turn dependent on phosphorylation of T145 of p21.46 Labeling: p21 (A–D) or pT145-p21 (E–H, red), cell nuclei (DAPI, blue), membranes (WGA, green).