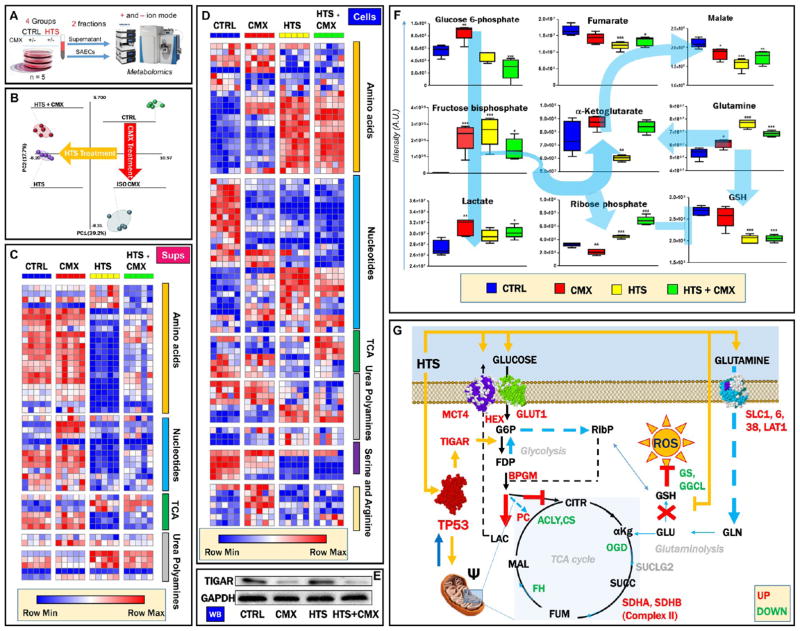
Figure 6.
HTS promotion of significant metabolic reprogramming UHPLC-MS metabolomics analyses were performed on SAECs cells and supernatants (n = 5, panel A). Partial least-squares-discriminant analysis shows significant alterations of the metabolic phenotype induced by the HTS and CMX treatments (B), as detailed by the heat maps for supernatants (C) and cells (D) showing impaired nucleotide metabolism and increased amino acid uptake and decreased amino acid catabolism in HTS-treated cells. In the heat map, Z-score normalized relative metabolite levels across samples are graphed in a blue-to-red (low-to-high) color coding. Western blot analysis showed that protein expression of TIGAR, a downstream target of the p53-p21 transcriptional axis, was induced by HTS alone (E). Specifically (F), this translated into increased steady-state levels of fructose bisphosphate, decreased glucose 6-phosphate, and increased ribose phosphate in HTS and HTS+CMX cells, suggestive of increased fluxes through the pentose phosphate pathway. The lowest levels of Krebs cycle intermediates were detected in HTS-treated cells, suggestive of depressed mitochondrial metabolism. Merging metabolomics data with results from proteomics analyses (G) indicated that HTS’s effect on glycolysis may be mediated by the up-regulation of glucose and lactate transporters (GLUT1 and MCT4), hexokinase, and biphosphoglycerate mutase. The effect on amino acid uptake in response to HTS treatment may be mediated by the increased protein expression of amino acid transporters (solute carriers SLC1, SLC6, SLC38, and large amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1, panel G). However, down-regulation of Krebs cycle (acetyl-coA lyase, citrate synthase, oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, and fumarate hydratase) and glutathione biosynthetic enzymes (γ glutamyl cysteine lyase and glutathione synthase) may contribute to explaining the metabolic observations on depressed Krebs cycle and decreased glutathione levels in response to HTS treatment (G).